|
⇤ ← Revision 1 as of 2014-11-27 14:42:52
Size: 1343
Comment:
|
Size: 1373
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 4: | Line 4: |
| The positional (= pointing) drifts are (with sufficient accuracy) linear, i.e. they can be described as | The positional (= pointing) drifts are (with sufficient accuracy) linear in (az,el), i.e. they can be described as |
| Line 6: | Line 6: |
| observedSorcePosInEl = a*observedSorcePosInAz + b | obsSorcePosInEl = a*obsSorcePosInAz + b |
| Line 8: | Line 8: |
| The figure below shows the positional offsets of all usable focus Lissajou maps relative to the source position for the fitted Z-focus. The 1mm (in red) and the 2mm (in green, upper left) data are shifted against each other because of the ~0.4mm focus difference between both arrays. The positional drifts while changing the Z-focus show a "butterfly" distribution (upper and bottom left). This is because the linear dependance observedSorcePosInEl(observedSorcePosInAz) changes the slope |
{{attachment:changeOfPointingWithZfoc.png}} The figure above shows the positional offsets relative to the source position for the fitted Z-focus of all usable focus Lissajou maps. The shift between the 1mm (in red) and the 2mm (in green, upper left) data is caused by the ~0.4mm focus difference between both arrays. The positional drifts while changing the Z-focus show a "butterfly" distribution (upper and bottom left). This is because the linear dependance obsSorcePosInEl(obsSorcePosInAz) changes the slope |
| Line 14: | Line 16: |
| {{attachment:changeOfPointingWithZfoc.png}} | |
| Line 16: | Line 17: |
| || {{attachment:focSlopeLow.png}} || {{attachment:focSlopeMed.png}} || {{attachment:focSlopeHig.png}} | {{attachment:focSlopeLow.png||width=600,height=400}} {{attachment:focSlopeMed.png||width=600,height=400}} {{attachment:focSlopeHig.png||width=600,height=400}} |
| Line 18: | Line 19: |
| Three examples for different slopes of observedSorcePosInEl(observedSorcePosInAz). Here the coordinates are relative to the pointing correctons. | Three examples for different slopes of obsSorcePosInEl(obsSorcePosInAz). Here the coordinates are relative to the pointing corrections. |
Change of the source position with Z-focus; RZ 27 Nov 2014
In the Lissajou maps performed to focus the telescope the source changes the position while changing the Z-focus. The positional (= pointing) drifts are (with sufficient accuracy) linear in (az,el), i.e. they can be described as
obsSorcePosInEl = a*obsSorcePosInAz + b
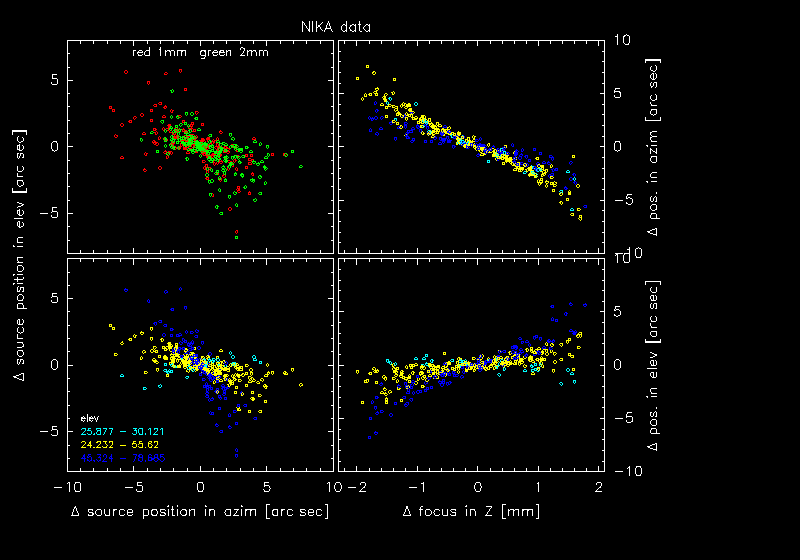
The figure above shows the positional offsets relative to the source position for the fitted Z-focus of all usable focus Lissajou maps. The shift between the 1mm (in red) and the 2mm (in green, upper left) data is caused by the ~0.4mm focus difference between both arrays. The positional drifts while changing the Z-focus show a "butterfly" distribution (upper and bottom left). This is because the linear dependance obsSorcePosInEl(obsSorcePosInAz) changes the slope with the elevation, i.e. it rotates in (az,el) with the elevation (bottom left). The two right figures show the positional drifts as function of the Z-focus changes relative to the fitted Z-focus correction.
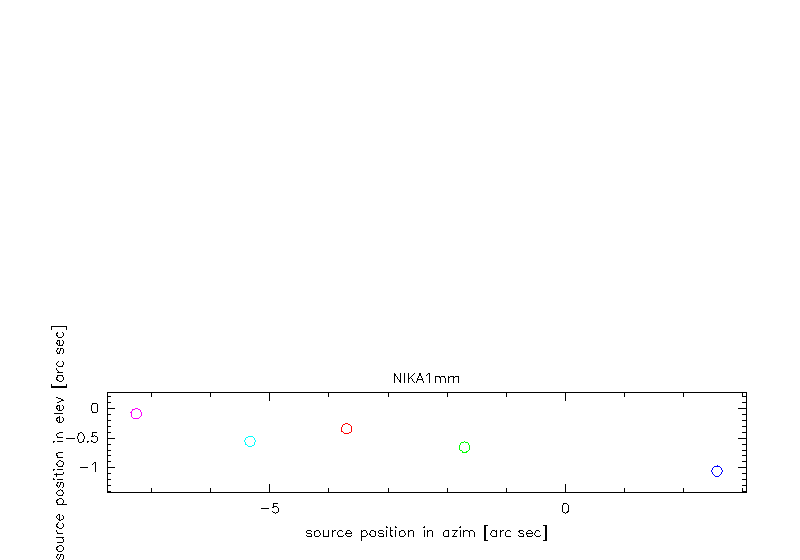
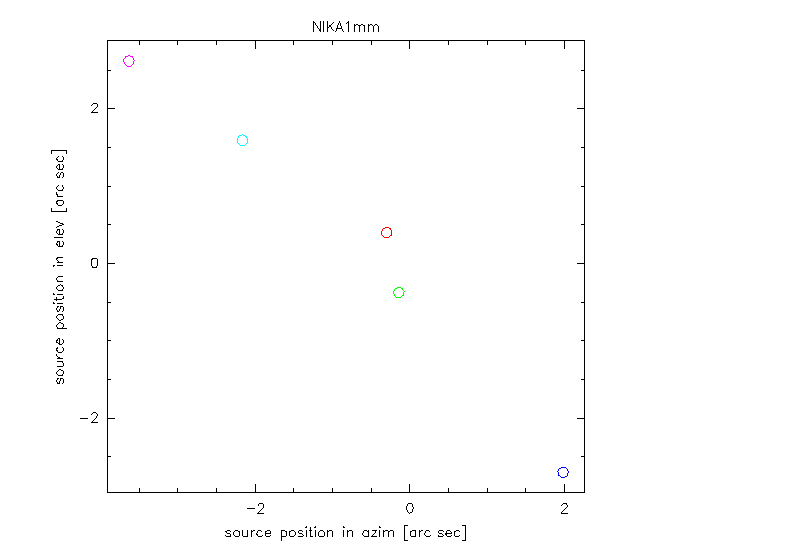
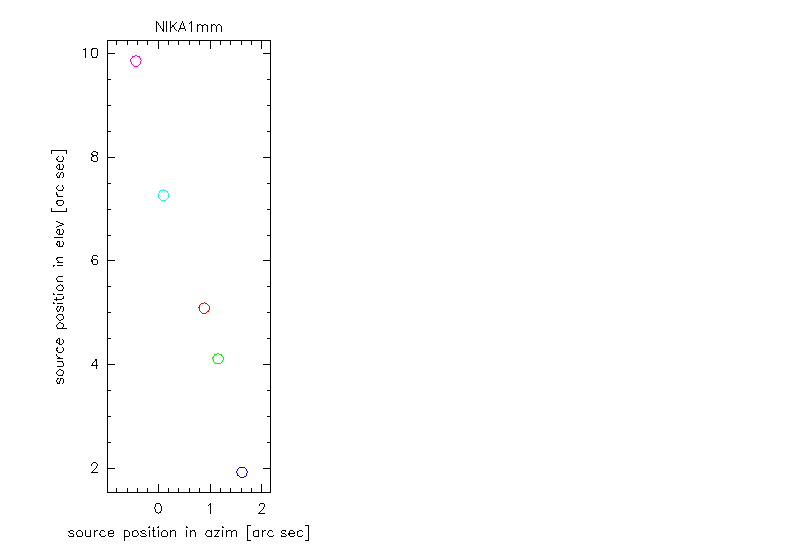
Three examples for different slopes of obsSorcePosInEl(obsSorcePosInAz). Here the coordinates are relative to the pointing corrections.
