|
Size: 25692
Comment:
|
Size: 25415
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 13: | Line 13: |
| ==== Nov-2011: 2SB for E2 and E3 (CK 6-Oct-2011) ==== | ==== Nov-2011: 2SB for E2 and E3 (CK 18-Oct-2011) ==== |
| Line 16: | Line 16: |
| er 8 GHz of instantaneous bandwidth per sideband and per polarization, whereas the single sideband (SSB) mixer on E150 has only a 4 GHz bandwidth per polarization. After the upgrade, the total EMIR bandwidth will increase from 64 to 104 GHz, of which up to 32 GHz will be available simultaneously. Below, comment (4) on Table 1, gives the '''new frequency ranges of E2 and E3'''. Figures 4.1. and 4.2 show the new bands, the new switch box scheme, and examples of '''band combinations''' which can be observed simultaneously. The new switch box will not allow for all possible band combinations. Below, we list some of those which will not be possible. | er 8 GHz of instantaneous bandwidth per sideband and per polarization, whereas the single sideband (SSB) mixer on E150 has only a 4 GHz bandwidth per polarization. Below, comment (4) on Table 1, gives the '''new frequency ranges of E2 and E3'''. Figures 4.1. and 4.2 show the new bands, the new switch box scheme, and examples of '''band combinations''' which can be observed simultaneously. |
| Line 49: | Line 49: |
| '''Recommendations for Observers:''' In general, we recommend using the lower sideband, as it often exhibits better receiver temperatures. Note that the lower frequency end of E3 (260-267GHz) has better receiver temperatures than the high end of E2. For details see the lab report of A.-L.Fontana (IRAM/Grenoble). <<BR>> | '''Recommendations for Observers:''' In general, we recommend using the lower sideband, as it often exhibits better receiver temperatures. Note that the lower frequency end of E3 (260-267GHz) has better receiver temperatures than the high end of E2. This will change with the upgrade in Nov-2011. <<BR>> |
Contents
-
EMIR Users Guide
- Upgrades
- Sky frequencies
- Overview
- EMIR bands
- EMIR observable band combinations after the upgrade in November 2011 (CK 17-Oct-2011)
- Focal plane geometry
- Selection of EMIR bands (Dichroics)
- IF Distribution (last update: July 2011)
- Connection to backends (last update: July 2011)
- Calibration issues
- Correct frequency scales over upto 24 GHz of bandwidth
- PaKo user interface (HU 2011-07-30)
- EMIR Observations Time Estimator
- Telescope efficiencies
- Status
- Commissioning Reports
- Friends of EMIR
EMIR Users Guide
Upgrades
Nov-2011: 2SB for E2 and E3 (CK 18-Oct-2011)
In November 2011, EMIR will be upgraded with dual sideband (2SB) mixers for bands E230 and E330, as it is currently the case for E090. These mixers cov er 8 GHz of instantaneous bandwidth per sideband and per polarization, whereas the single sideband (SSB) mixer on E150 has only a 4 GHz bandwidth per polarization. Below, comment (4) on Table 1, gives the new frequency ranges of E2 and E3. Figures 4.1. and 4.2 show the new bands, the new switch box scheme, and examples of band combinations which can be observed simultaneously.
Jul-2011: 32GHz IF-system, FTS backends
Since July 2011, we have made available a new 32GHz IF system which includes 24 fast fourier transform spectrometers (FTS). This upgrade has duplicated the amount of instantaneous bandwidth available at the 30m telescope. 16 GHz of bandwidth can now be used instantaneously, in both polarisations. Eight cables of 4GHz width now carry the intermediate frequencies through the telescope cable spiral to the backend room. The full 32GHz of bandwidth are covered by 24 FTS working at 200kHz resolution. This improves the available velocity resolution over large bandwidths by a factor of 10 compared to WILMA with its 2MHz resolution. It is now possible to observe at 0.6km/s resolution in the 3mm band allowing to resolve star forming clouds in the Milky Way and in nearby galaxies. The resolution of the 24 FTS can further be increased to 50 kHz, in which case only the inner 1.82GHz of the 4GHz EMIR bands are covered. The previous 4x4GHz system is still in use, and the additional 4x4GHz cables are connected to the outer 4GHz wide bands of EMIR 3mm channel, i.e. to E0UO and E0LO in both polarisations. All FTS units work either at 200 kHz or at 50 kHz. However it is not possible to set them individually to different resolutions. The new FTS can also be connected to the 2x9 HERA cables of 1GHz width, both at 200kHz or at 50kHz resolution. See also the call for proposals for the deadline in September 2011.
See a brief report further below, and an overview of available backends, including the new broad band continuum (bbc) backend and the new IF distribution.
Sky frequencies
Before the upgrade of E2 and E3 in November 2011
EMIR |
Fsky |
mixer |
polar- |
IF width |
Trx |
Gim |
|
combinations |
Trx |
Remark |
|||
band |
GHz |
type |
isation |
GHz |
K |
dB |
|
E0/2 |
E1/3 |
E0/1 |
K |
|
|
E0 |
83-117 |
2SB |
H/V |
8 |
50 |
>10 |
|
X |
|
X |
65 |
|
(1) |
E1 |
129-174 |
SSB |
H/V |
4 |
50 |
>10 |
|
|
X |
X |
65 |
|
(2) |
E2 |
201-267 |
SSB |
H/V |
4 |
50 |
>10 |
|
X |
|
|
65 |
|
(4) |
E3 |
260-348 |
2SB |
H/V |
4 |
70 |
>10 |
|
|
X |
|
85 |
|
(3, 4) |
After the upgrade of E2 and E3 in November 2011
EMIR |
Fsky |
mixer |
polar- |
IF width |
Trx |
Gim |
|
combinations |
Trx |
Remark |
|||
band |
GHz |
type |
isation |
GHz |
K |
dB |
|
E0/2 |
E1/3 |
E0/1 |
K |
|
|
E0 |
83-117 |
2SB |
H/V |
8 |
50 |
>10 |
|
X |
|
X |
65 |
|
(1) |
E1 |
129-174 |
SSB |
H/V |
4 |
50 |
>10 |
|
|
X |
X |
65 |
|
(2) |
E2 |
202-274 |
2SB |
H/V |
8 |
50(?) |
>10 |
|
X |
|
|
65 |
|
(4) |
E3 |
277-352 |
2SB |
H/V |
8 |
70(?) |
>10 |
|
|
X |
|
85 |
|
(3, 4) |
Table 1: EMIR Frontend. Sky frequencies Fsky are given for the centers of the outermost 4GHz IF bands (cf. Fig.3 and 4). Acronyms: 2SB - dual sideband mixers, SSB - single side band mixers, H/V -- horizontal and vertical polarizations, Trx is the SSB receiver temperature in single sideband observations, Gim is the image band rejection. Note that the receiver noise is somewhat increased when observing with two bands simultaneously due to the dichroic elements needed for these observations (see below for more details).
(1) At frequencies below 83GHz, the receiver gain ratio is known to vary strongly over the bandpass and between the two polarisations. In addition, the receiver noise temperatures increase.
(2) Sky frequencies between 174 and 189 GHz have been successfully tested (Sep-09, 19-Sep-11) and may be available on special request. At the highest frequencies the receiver temperatures increase to about 130K and the sideband gain-ratio is not well known.
(3) A new local oscillator oscillator for the E330 band has been installed at the 30m on 17-Nov-2009. Band 4 has been commissioned Nov 09 - Feb 2010 (Reports). Frequencies above 348GHz are not accessible. This upper frequency limit of E3 is given by the limitations of the Local Oscillator which will not be changed for the upgrade in Nov-2011. As described in the commissioning report, the LO shows instabilities at a few frequencies. If you as observer encounter such problems, please contact the operator and/or receiver engineer. Swapping the sideband may help.
Recommendations for Observers: In general, we recommend using the lower sideband, as it often exhibits better receiver temperatures. Note that the lower frequency end of E3 (260-267GHz) has better receiver temperatures than the high end of E2. This will change with the upgrade in Nov-2011.
(4) In November 2011, EMIR bands E2 and E3 will be upgraded to full dual-polarisation, dual-sideband 8GHz each mixers. The frequency ranges will change, in particular the overlap region between E2 and E3. The new frequency ranges of E2 are 202-274 and 277-352 for E3. We give here the centers of the outer bands which are reachable by all backends including VESPA. The FTS at 200kHz can reach frequencies which lie 2GHz further out. Still higher frequencies of E3 are currently inaccessible because of the limitations of the local oscillator.
Overview
The new receiver EMIR (Fig.1) has been installed and commissioned at the 30m telescope in March through April 2009. EMIR replaced the single pixel heterodyne receivers A/B100, C/D150, A/B230, and C/D270. HERA, the bolometers, and the backends are unchanged. EMIR provides a minimum instantaneous bandwidth of 4 GHz in each of the two orthogonal linear polarizations for the 3, 2, 1.3 and 0.9mm atmospheric windows (Fig.2). In addition to the vast increase in bandwidth, the receiver is expected to offer considerably improved noise performance, a stable alignment between bands, and other practical advantages.
The four EMIR bands are designated as E090, E150, E230, and E330 according to their approximate center frequencies in GHz. While the E150 and E230 bands have SSB mixers with a single sideband available at a time, the E090 and E330 bands can be operated in 2SB mode where both sidebands are available for connection to backends. Furthermore, the E090 band is built in a technology that offers 8 GHz instantaneous bandwidth per sideband and polarization. Both polarizations of a given band will always be tuned to the same frequency as they share a single common local oscillator. The tuning ranges of the 4 bands, the typical receiver noise temperatures, and other parameters are listed in Tab.1.
EMIR provides for the first time in the history of the 30m telescope a permanently available high sensitivity E330 band, opening this atmospheric window for regular use under good weather conditions. See the commissioning report below.
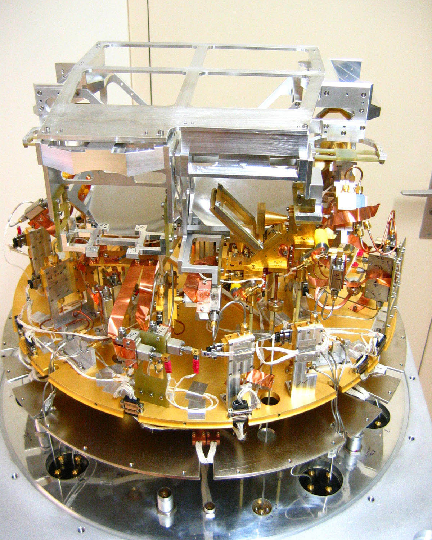
Figure 1: EMIR during final integration in the Grenoble receiver laboratory. One of the four dual-polarization mixer pairs is visible near the center of the photograph. The beams of the 4 mixer pairs leave the dewar through 4 separate windows towards the top of the figure. Warm optics (not shown) can combine some of the 4 beams for observation of the same position on the sky.
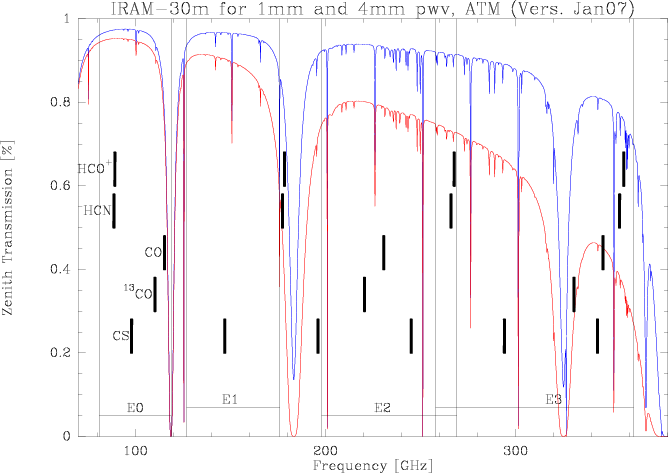
Figure 2: Atmospheric transmission between 60 and 400GHz for two precipitable water vapors, modeled with the ATM model. The EMIR bands are marked together with the frequencies of a few important molecular transitions.
EMIR bands
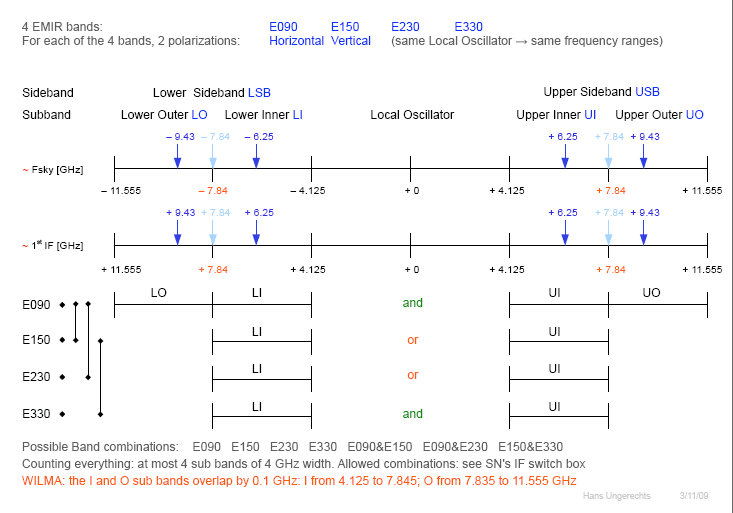
Figure 3: Visual overview of EMIR bands currently available, i.e. before the upgrade planned for November 2011.
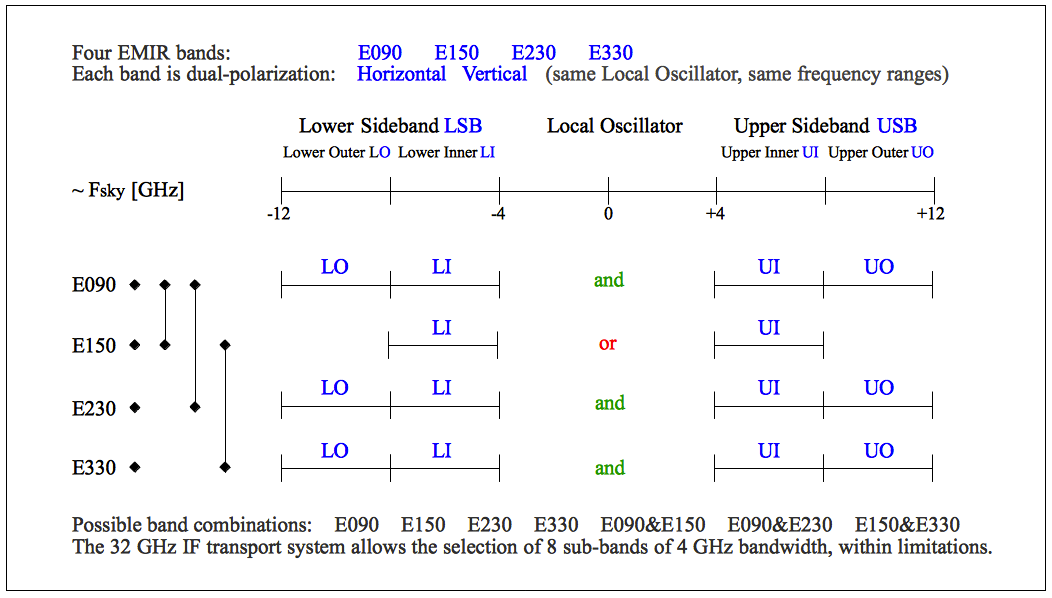
Figure 4.1: Overview of EMIR bands after the upgrade of E2 and E3 planned for November 2011. The frequencies given at the edges of the bands should be considered as indications only since they will likely slightly change in the future.
EMIR observable band combinations after the upgrade in November 2011 (CK 17-Oct-2011)
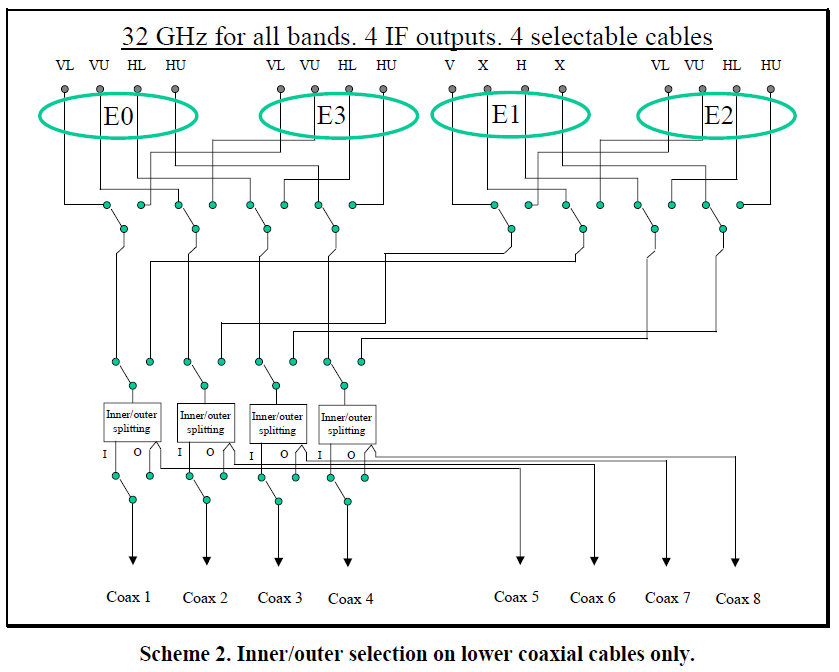
Figure 4.2: Overview of band combinations observable after the Nov 2011 upgrade (with a new switching box).
EMIR has four different bands covering the four main atmospheric windows in the millimetre range: E090, E150, E230 and E330. Dual band observation is possible but only the E0/E1, E0/E2 and E1/E3 band combinations are allowed by the receiver optics. After the upgrade in November 2011, bands E0, E2 and E3 have four IF outputs each: 2 polarizations (H,V) and 2 sidebands (L,U), each of them is 8 GHz wide. Band E1 has only two IF outputs, 4 GHz wide each, of different polarizations but same sideband. The 8GHz wide IF outputs are split in two blocks, 4 GHz wide each, denoted by I and O (inner and outer) and sent to the spectrometers by the use of in total 8 coaxial cables. This means that a total of 32GHz of bandwidth are transferred to the spectrometers. A future upgrade to 64GHz allowing simultaneous observations of E0 and E2 with all bands, is planned.
When designing the new switch box, we assumed that most, if not all observers use both polarisations simultaneously.
- General band selection rules:
- Only four IF outputs (of 8GHz for E0, E2, E3, or of 4GHz for E1), from a single receiver or any of the band combinations E0/E1, E0/E2, E1/E3, can be used simultaneously.
- Only a maximum of 4 inner bands can be selected.
- The lower 4 coaxial cables can be connected to the inner or outer bands of the previously selected IF outputs. The other four cables are fixed and can be only connected to the outer bands.
- Selection of IF outputs is restricted by the following exclusion table (RxA+RxB refer to E0/E1, E0/E2 or E1/E3):
- VL on RxA excludes the use of VU on RxB
- VU on RxA excludes the use of VL on RxB
- HU on RxA excludes the use of HL on RxB
- HL on RxA excludes the use of HU on RxB
- WILMA, 4MHz, and VESPA can only be connected to the first 4 cables.
- Possible setups after the Nov 2011 upgrade:
One full band (E0 or E2 or E3): LI+LO, UI+UO dual-pol. (for line surveys)
- E0/E2:
E0: UI+UO, E2: UI+UO (e.g. 12CO, 13CO 1-0, 12CO 2-1, dual-pol)
E0: LI+LO, E2: LI+LO (e.g. HCN, HCO+ 1-0, 13CO 2-1, dual-pol)
E0VUO (12CO 1-0), E2VUI, E2HUI (12CO 2-1), E2HLI (13CO & C18O 2-1) [only 4 cables used]
E2HLI, E2HUI, E0VUI (or any other E0V band) (12CO & 13CO 2-1 + one 3mm line) [only one polarisation]
E0U I/O H/V (12CO,13CO,C18O 1-0), E2U I/O H/V (12CO 2-1) (200kHz, not: 50kHz)
- E1/E3:
- 4GHz dual pol with E1 and with E3 (like before Nov-11, only 4 cables)
- E0/E1: Using both polarisations of one of the inner bands of E1, blocks the 2nd and 4th IF cables and leaves only the possibility to observe both polarisations of the lower E0 band, inner and outer, e.g.
- E1LIV, E1LIH, E0LIV, E0LIH, E0LOV, E0LOH (upper band of E0 is excluded, important application: CS 2-1, 3-2)
- E0LOH, E0LIV, E0UIH, E1LIV (special setup, as only one polarisation of E1LI is used, one winter proposal)
Setups which are not possible (even after the EMIR upgrade in Nov-2011):
Both sidebands/same polarisation: 3mm: UI+UO, 1mm: LI+UI (12CO, 13CO 1-0 & 2-1)
- E0 LI,UI + E2 LI,UI (only a maximum of 4 inner bands can be selected), in general, when connecting to E2 LI+UI with both polarisations, none of the inputs of E0 are accessible.
- E0 LO UO + E2 LO LI, in general, when connecting to the lower *and* outer bands of E0, it is not possible to also connect to E1 or E2 or E3.
- 50kHz FTS: C18O, 13CO, 12CO 1-0 simultaneously. These lines lie 5.49GHz apart, while the outer edges of the FTS 50kHz units in the inner and outer band of EMIR lie 5.42GHz apart. The inner edges lie 1.78GHz apart. However, it is no problem to observe these lines simultaneously with 200kHz resolution.
Focal plane geometry
The four bands will be combined in only two possible beams (left and the right beams when looking to the cryostat front face). The left and right beams are offset by about 90" on the sky. See the telescope status page for the present Nasmyth offsets (cf. EMIR Commissioning report below). Observations are carried out with either of the two beams. Simultaneous observations with both beams are at present not supported.
Selection of EMIR bands (Dichroics)
 Before reaching the Nasmyth mirrors, the four beams of the EMIR bands pass through warm optics that contains switchable mirrors and dichroic elements for redirection of the beams towards calibration loads and for combining beams. In its simplest mode, the warm optics unit selects one single EMIR band for observation. This mode avoids the use of the slightly lossy dichroic elements and therefore offers the best receiver noise temperatures.
Before reaching the Nasmyth mirrors, the four beams of the EMIR bands pass through warm optics that contains switchable mirrors and dichroic elements for redirection of the beams towards calibration loads and for combining beams. In its simplest mode, the warm optics unit selects one single EMIR band for observation. This mode avoids the use of the slightly lossy dichroic elements and therefore offers the best receiver noise temperatures.
Three dichroic mirrors are available for combining either the E090 and E150 beams, or the E090 and E230 beams, or the E150 and E330 beams (Table 1). The combination of bands is not polarization selective, i.e. the combined bands will stay dual polarization. The loss of these dichroics increases however the receiver temperatures by, in general, only 10 - 15 K. The losses of E2 (due to the use of the dichroic) are higher than 10% for frequencies above ~258GHz and below ~202GHz (cf. Table 2). The polarization angle of the dichroic was chosen to minimize the losses for 231GHz. The observer is therefore adviced to carefully evaluate whether an observation involving two different bands is more efficiently made in parallel or in series.
Note that simultaneous observations of e.g. HCO+ at 89.7 and 266.5GHz with E0 and E2, will suffer from much increased system temperatures in E2, due to the losses of the dichroics using this frequency combination.
The dichroics are needed for dual-band observations with EMIR. The following table shows the losses of the dichroics, based on a separate mixer and dichroic characterization done in the receiver lab by Anne-Laure Fontana in Feb 09. This table is subject to change with new measurements of the integrated receiver, and with new dichroics.
Table 2: Performance of dichroics (February 2009, Report of Anne Laure):
E0/E2 |
E0/E1 |
E1/E3 |
|||||||||
E0 |
E0 |
E2 |
E2 |
E0 |
E0 |
E1 |
E1 |
E1 |
E1 |
E3 |
E3 |
GHz |
% |
GHz |
% |
GHz |
% |
GHz |
% |
GHz |
% |
GHz |
% |
84-108 |
2.5 |
202 |
10 |
84 |
4 |
129 |
5 |
129-138 |
2.5 |
261-357 |
<2.5 |
116 |
<2 |
213 |
5 |
92 |
3.2 |
138-156 |
1 |
147 |
4.5 |
369 |
7 |
|
|
225 |
3 |
100-110 |
5 |
168 |
2 |
156 |
3.5 |
|
|
|
|
231 |
2 |
110-115 |
~10 |
171 |
2 |
174 |
2.5 |
|
|
|
|
243 |
5 |
|
|
174 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
255 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
258 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
267 |
50(!) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each percent of losses, increases the receiver temperature by about 4K.
IF Distribution (last update: July 2011)
The IF switch box in the receiver cabin allows to select 4 EMIR channels of 4 GHz bandwidth each from 16 inputs. The 4 channels of 8 GHz width available from E090 are rearranged by the IF switch box into 4 pairs of inner and outer 4 GHz wide channels. The box can handle all plausible single band observations as well as the band combinations indicated in Table 1. Note that the IF switch box has not been changed for the upgrade to a 32GHz IF system. The four new IF cables are not connected to the switch box, but directly to the four outer EMIR bands. Here is a plot of the current scheme.
The following table shows possible band combinations with EMIR, which are allowed by the IF switch box (Santiago Navarro 13.2.2009): BAND_COMBINATIONS.pdf.
An overview of the frequency distribution of the entire system is given here.
Connection to backends (last update: July 2011)
Four output channels are sent via the IF cables to a backend distribution unit which provides copies of these 4 channels to a range of backends processors which then prepare the IF signals for distribution to the spectrometers. Three backend processors have been build to feed the new 4 GHz wide IF channels to the existing backends:
The WILMA processor rearranges the four incoming 4 GHz wide IF channels into 16 channels of 1 GHz width which can be processed by 16 WILMA autocorrelator units. Since each unit provides 512 spectral channels of 2 MHz, sufficient backend power is available at low spectral resolution for full coverage of the 4x4GHz bottleneck.
The 4 MHz processor rearranges any two incoming 4 GHz wide IF channels into 8 slices of 1 GHz width for processing in 8 units of the 4 MHz filter bank. 2x4 GHz of EMIR bandwidth are thus covered at 4 MHz resolution.
The narrow backend processor prepares the 4 incoming IF channels for input into VESPA. Only the central part of the 4 GHz IF channels is accessible to these backends. Inside this central part (1 GHz for the filterbank and 640 MHz for VESPA), these backends can be configured as before. The VLBI terminal is also fed from this processor.
The 24 fast fourier transform spectrometers (FTS) are handled separately.
Backends at the IRAM 30m telescope
Calibration issues
EMIR comes with a new calibration system. The external warm optics provides ambient temperature loads and mirrors reflecting the beams back into the 15 K stage of the cryostat. This system is expected to be very reliable and constant over time. Absolute calibration accuracy will be better than 10% with EMIR when all details are well settled.
Bands E150 and E230 have backshort tuned single-sideband mixers; DSB tuning is not possible, but sidebands (USB or LSB) may be selectable within limitations. The image rejection is better than 10 dB for all frequencies. On-site measurements of the rejection is not longer straightforward for these mixers, since the Martin--Puplett interferometers are not available anymore. As the optimum way of calibrating the image rejection is still under exploration, users who propose observations which rely on an enhanced accuracy of calibration of image gains should mention this request in the proposal.
Bands E090 and E330 have tunerless sideband separation mixers, allowing simultaneous observations of both sidebands in separate IF bands. These mixers have been characterized in the laboratory for their image rejection and are expected to have the same performance on site (>13dB).
Correct frequency scales over upto 24 GHz of bandwidth
It is common practice at radio observatories to correct the frequency of an observation for the strongly time variable velocity of the Observatory with respect to the solar system barycenter. This guarantees that lines observed near the Doppler-tracked frequency, usually the band center, always have the correct barycentric velocity, independent of the time of observation. However, the effect of the Observatory's motion on the velocity scale at frequencies which are far from the Doppler-tracked frequency, is usually ignored.
This effect which is of the order of 1e-4 cannot be neglected anymore if large bandwidths are used, as with EMIR. The worst case occurs with band E090 where channels as far away as 20 GHz need to be considered if a velocity channel in one of the sidebands is Doppler-tracked. In unfavorable but nevertheless frequent cases (target source not too far from the ecliptic, like the Galactic center), shifts of up to +/-2 MHz occur. In principle, CLASS corrects the shifts. However, as the report below describes, these shifts correspond to time variable changes of the frequency resolution. Co-adding or averaging spectra taken at different times, may then lead to a broadening of the effective frequency resolution.
Accurate line center frequencies: Report of 03-Aug-2011 by Buchbender, Kramer et al.. Two bugs in mira and class caused frequency shifts and have been corrected for. The new versions of mira and class were installed at the 30m on 16-Aug-2011.
PaKo user interface (HU 2011-07-30)
The observer interface program PaKo was upgraded for the introduction of EMIR.
2011-07-30: After the installation of the new 32GHz FTS system, some commands have changed, in particular the BACKEND command, for details see v1.1.6 of the PaKo Manual and demo scripts.
Note that older versions of PaKo documentation are still available, e.g., the original upgrade for the introduction of EMIR in 2009.
Please contact your astronomer-of-duty to help you prepare scripts or in case of any questions.
EMIR Observations Time Estimator
Telescope efficiencies
Status
Commissioning Reports
Bands 1-3 (April 2009)
Bands 1-3: EmirCommissioningReportVers1.1.pdf
Band 4 (April 2010)
Band 4: emir-e3-com-report-05apr2010.pdf.
Polarimetry (Bands 1 and 3, August 2010)
Upgrade to 32GHz FTS system (July 2011)
Friends of EMIR
During the first half of the 2009 summer semester, each EMIR project had an IRAM astronomer assigned to it, to help with setting up the scripts and observations. See here: Friends of EMIR Projects. This extra service is not continued. Instead, we now provide template scripts and an updated PaKo manual.
This page is maintained by C.Kramer. Any comments are welcome.

