|
Size: 11152
Comment:
|
Size: 42862
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 3: | Line 3: |
| #acl CarstenKramer:read,write,delete,revert,admin All: [[TableOfContents(5)]] == EMIR (Eight MIxer Receiver) == === Call for Proposals === ==== Overview ==== The new receiver EMIR (Fig.1) is scheduled for installation and commissioning at the 30m telescope in March through April 2009. EMIR will replace the current single pixel heterodyne receivers A/B100, C/D150, A/B230, and C/D270. HERA, the bolometers, and the backends are unchanged. EMIR will provide a minimum instantaneous and width of 4 GHz in each of the two orthogonal linear polarizations for the 3, 2, 1.3 and 0.9mm atmospheric windows (Fig.2). In addition to the vast increase in bandwidth, the receiver is expected to offer considerably improved noise performance, a stable alignment between bands, and other practical advantages. The four EMIR bands are designated as E090, E150, E230, and E330 according to their approximate center frequencies in GHz. While the E150 and E230 bands have SSB mixers with a single sideband available at a time, the E090 and E330 bands can be operated in 2SB mode where both sidebands are available for connection to backends. Furthermore, the E090 band is built in a technology that offers 8 GHz instantaneous bandwidth per sideband and polarization. Both polarizations of a given band will always be tuned to the same frequency as they share a single common local oscillator. The tuning ranges of the 4 bands, the typical receiver noise temperatures, and other parameters are listed in Tab.1. EMIR will for the first time in the history of the 30m telescope provide a permanently available high sensitivity E330 band, opening this atmospheric window for regular use under good weather conditions. As commissioning of this channel will be difficult and time consuming during the summer semester, only a maximum of total 20 hours observing time will be available for regular proposals for this semester. The proposed targets should ideally be pointlike and available during nighttime in fall. The observations will be made as service observing with shared risk. At the time of writing, EMIR is undergoing final tests in the receiver laboratory. Precise figures of EMIR's performance at the telescope will not be known before the proposal deadline. The Observatory will nevertheless make an effort to publish the results of the commisisoning available as soon as possible on this wiki page. The interested astronomer may also find more detailed technical information on EMIR under this URL. IRAM staff is also available to help astronomers with the preparation of EMIR (and other) proposals. attachment:emir-optics.png [[BR]] '''Figure 1''': EMIR during final integration in the Grenoble receiver laboratory. One of the four dual-polarization mixer pairs is visible near the center of the photograph. The beams of the 4 mixer pairs leave the dewar through 4 separate windows towards the top of the figure. Warm optics (not shown) can combine some of the 4 beams for observation of the same position on the sky. attachment:plot-iram30mv2.png [[BR]] '''Figure 2''': Atmospheric transmission between 60 and 400GHz for two precipitable water vapors, modeled with the ATM model. The EMIR bands are marked together with the frequencies of a few important molecular transitions. '''Table 1''': EMIR Frontend. Sky frequencies Fsky are given for the center of the IF band. 2SB dual sideband mixers, SSB - single side band mixers, H/V -- horizontal and vertical polarizations, Trx is the SSB receiver temperature in single band observations ({\it left}). For dual-band observations, Trx includes a 15K noise contribution from the dichroics (right). [[BR]] ||'''EMIR''' ||'''Fsky''' || '''mixer''' || '''polar-''' ||'''IF width''' || '''Trx''' || '''Gim''' || ||||||<style="TEXT-ALIGN: center">'''combinations''' ||'''Trx''' || || '''band''' || '''GHz''' || '''type''' || '''isation''' || '''GHz''' || '''K''' || '''dB''' || || '''E0/2''' || '''E1/3''' || '''E0/1''' || '''K''' || ||E0 ||83-117 ||2SB ||H/V ||8 || 50 || 13 || || X || || X || 65 || ||E1 ||129-174 ||SSB ||H/V ||4 || 50 || 13 || || || X || X || 65 || ||E2 ||200-267 ||SSB ||H/V ||4 || 50 || 13 || || X || || || 65 || ||E3 ||260-360 ||2SB ||H/V ||4 || 50 || 13 || || || X || || 85 || ==== Selection of EMIR bands ==== Before reaching the Nasmyth mirrors, the four beams of the EMIR bands pass through warm optics that contains switchable mirrors and dichroic elements for redirection of the beams towards calibration loads and for combining beams. In its simplest mode, the warm optics unit selects one single EMIR band for observation. This mode avoids the use of the slightly lossy dichroic elements and therefore offers the best receiver noise temperatures. Three dichroic mirrors are available for combining either the E090 and E150 beams, or the E090 and E2230 beams, or the E150 and E330 beams (Tab.1). The combination of bands is not polarization selective, i.e. the combined bands will stay dual polarization. The small loss of these dichroics increases however the receiver temperatures by 10 - 15 K. The observer is therefore adviced to carefully evaluate whether an observation involving two different bands is more efficiently made in parallel or in series. ==== Connection to backends ==== The remarkable bandwidth of EMIR of altogether 64 GHz faces 2 limitations of the existing 30m hardware: (1) the four IF cables can transport only 4 GHz each (the $4\times4$ GHz bottleneck) and (2) only at low spectral resolution are there enough backends to cover the 16 GHz which pass through the bottleneck. A new '''IF switch box''' in the receiver cabin allows to select 4 EMIR channels of 4 GHz bandwidth each from 16 inputs. The 4 channels of 8 GHz width available from E090 are rearranged by the IF switch box into 4 pairs of inner and outer 4 GHz wide channels. The box can handle all plausible single band observations as well as the band combinations indicated in Tab.1. A full list of possible switch settings is available on the 30m web site. The selected 4 output channels are sent via the IF cables to a new '''backend distribution unit''' which provides copies of these 4 channels to a range of backends processors which then prepare the IF signals for distribution to the spectrometers. Three new backend processors have been build to feed the new 4 GHz wide IF channels to the existing backends: * The '''WILMA processor''' rearranges the four incoming 4 GHz wide IF channels into 16 channels of 1 GHz width which can be processed by 16 WILMA autocorrelator units. Since each unit provides 512 spectral channels of 2 MHz, sufficient backend power is available at low spectral resolution for full coverage of the 4x4GHz bottleneck. * The '''4 MHz processor''' rearranges any two incoming 4 GHz wide IF channels into 8 slices of 1 GHz width for processing in 8 units of the 4 MHz filter bank. 2x4 GHz of EMIR bandwidth are thus covered at 4 MHz resolution. * The '''narrow backend processor''' prepares the 4 incoming IF channels for input into the 1 MHz filterbank and VESPA. Only the central part of the 4 GHz IF channels is accessible to these backends. Inside this central part (1 GHz for the filterbank and 640 MHz for VESPA), these backends can be configured as before. The VLBI terminal is also fed from this processor. ==== Calibration issues ==== EMIR comes with a new calibration system. The external warm optics provides ambient temperature loads and mirrors reflecting the beams back into the 50 K ('''CHECK''') stage of the cryostat. This system is expected to be very reliable and constant over time. Absolute calibration accuracy will be better than 10% with EMIR when all details are well settled. Bands E150 and E230 have backshort tuned single-sideband mixers; DSB tuning is not possible, but sidebands (USB or LSB) may be selectable within limitations. The image rejection is better than 10 dB for all frequencies. On-site measurements of the rejection is not longer straightforward for these mixers, since the Martin--Puplett interferometers are not available anymore. As the optimum way of calibrating the image rejection is still under exploration, users who propose observations which rely on an enhanced accuracy of calibration of image gains should mention this request in the proposal. Bands E090 and E330 have tunerless sideband separation mixers, allowing simultaneous observations of both sidebands in separate IF bands. These mixers have been characterized in the laboratory for their image rejection and are expected to have the same performance on site (>13dB). ==== Velocity scales ==== It is common practise at radio observatories to correct the frequency of an observation for the strongly time variable velocity of the Observatory with respect to the solar system barycenter. This guarantees that lines observed near the Doppler-tracked frequency, usually the band center, always have the correct barycentric velocity, independent of the time of observation. However, the effect of the Observatory's motion on the '''velocity scale''' which affects most the velocity channels farthest away from the Doppler-tracked frequency, is usually ignored. This effect which is of the order of 1e-4 cannot be neglected anymore if large bandwidths are used, like with EMIR. The worst case occurs with band E090 where channels as far away as 12 GHz need to be considered if the LO frequency is Doppler-tracked. In unfavorable but nevertheless frequent cases (target source not too far from the ecliptic, like the Galactic center), errors of up to +/-1.2MHz occur. Since the magnitude of the error changes with time, narrow spectral lines may be broadened after a few hours of observation. Observers concerned by this complication may consult this wiki (further below) for further details and solutions. ==== Update of PaKo ==== Work is in progress to adapt the observer inface program Pako for EMIR. In particular, the receiver command and the connectivity to backends need to be updated. Documentation will be made available [http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/ncs30m/ here]. ==== Observations time estimator ==== The GILDAS group has prepared a new 30m time estimator for EMIR. It is now part of the GILDAS software package and accessible via ASTRO. For download of the GILDAS package please connect to [http://www.iram.fr/IRAMFR/GILDAS/ here] and follow the instructions. For HERA and MAMBO2, the old web based time estimator is still available [http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/obstime/time_estimator.html here]. Note that a web based estimator for EMIR will be made available for the next deadline. As commissioning of EMIR has not yet started at the time of writing, the new time estimator is based on the laboratory performance of EMIR and the ''expected'' losses at the telescope. === Details === ==== Losses of dichroics ==== ==== Settings of the IF switch box ==== ==== Velocity scales ==== ==== Results of Commissioning ==== TBD |
#acl PabloTorne,CarstenKramer:read,write,delete,revert,admin ClemensThum:read KarlSchuster:read GabrielPaubert:read AlbrechtSievers:read All:read <<Anchor(beginOfPage)>> <<TableOfContents(5)>> == EMIR Users Guide == === News (last update: 25-Apr-2017, CM) === * A filter was installed in the E230 band on 14-Feb-2017, suppressing unwanted harmonics of the LO (see [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|here]]), which had been generating spurious lines. Other (weak) harmonics created later in the chain cannot be suppressed by the current filter. <CM, 25-Apr-2017> * After an exchange of compressors, the mixer temperature of EMIR is back to 3.7K. <24-Apr-2017> * We have received reports of spurious lines in the E230 band of EMIR. Two independent reasons have been identified: (1) change of mixer biasing because of slightly increased physical temperatures (about 4.2K) after exchange of cold head last year. (2) Unwanted harmonics of the fundamental frequency of the local oscillator ([[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|see report of Jan. 2017]]). To tackle item (1), we plan to update the tuning table. And for item (2), we plan to install a filter, as we had done in the past for the local oscillator of E090 and E150. <18-Jan-2017> * Since 17-January 2017, the dichroic mirror D24 is kept in place not only for E1/E3 observations, but also when observing only with E330. See the report by [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|H.Ungerechts of 1-February]]. * In mid February 2017 (date changed), we plan to change the online data processing from MIRA to MRT-CAL for most of the data. Exceptions are XPOL/EMIR data, and continuum data (e.g. pointing, focus, skydips). There will be a few subtle changes. See '''Tutorials''' on the [[http://www.iram.fr/IRAMFR/GILDAS/|GILDAS home page]]. MRT-CAL is alreay included into the GILDAS package, and, for the foreseeable future, MIRA will stay available. * E150: On 9-August 2016, a filter was installed at the output of the E1 local oscillator box in order to suppress generated harmonics of the Gunn fundamental frequency. Lop1 attenuator values were also modified in the LO tuning table in order to compensate for the extra power loss introduced by this filter/waveguide combination. Gunn frequencies @ (67.75, 74.0, 80.0, 81.0, 87.0) GHz was checked and sufficient power was obtained to pump the mixers. (Total LO 135.5, 148.0, 160.0, 162.0, 174.0)GHz. (DJ 10-Aug) The spurious line which had been detected in Dec 2015 ( [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|Marka & Kramer, Dec-2015]]) is not seen anymore. The rejection is better than -34dB. (SN 11-Aug). * EMIR frequency setups can now be prepared using a new set of commands in ASTRO\PICO (GILDAS versions of July 2016 or younger). These take into account the available frequency limits, band combinations, and spectrometers, and plot the covered frequency ranges together with known spectral lines, taking into account source velocities or redshifts. This new functionality is still under development and is likely to be upgraded in the future. Examples are given [[http://www.iram.fr/~gildas/demos/astro/demo-astro.pdf|here]], but see also the online help. * After the upgrade of the E0 and E1 bands in November 2015, the alignment between bands has somewhat degraded, as also the relative focus offsets ([[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|Marka & Kramer, Dec-2015]]). * Spectroscopic polarimetry observations in bands E0 and E1 show an increase of the instrumental circular polarisation for reasons not yet understood (see [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/PolarimetryforAstronomers|here]]). For older news check [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Historic_news|here]]. === Upgrades === ==== Sep-2016: New dichroic for E0/E2 dual-band operation ==== During heavy maintenance end of September 2016, we have installed a new dichroic mirror for E0/E2 dual-band operation, which is strongly improving receiver noise temperatures in dual-band observations at the high frequency end of E230 above 240GHz, compared to the numbers of 2009 given in Table 2 below. In particular, this will allow efficient observations simultaneously of the 1-0 and 3-2 transitions of HCN, HNC, HCO+. See the report by [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|H.Ungerechts of 1-February-2017]]. ==== Dec-2015: New 2SB mixers for E0 and E1 ==== EMIR bands E090 and E150 have been upgraded end of November 2015. Mixers have been replaced by NOEMA-type mixers. For E090, an ortho-mode transducer with one horn only, splits both polarisations. The frequency range of E090 has been extended down to almost 70GHz (see details below). Commissioning has shown that in general the upgrade went well. See further comments in the news section. ==== Sep-2013: 2SB mixers for E1 ==== We exchanged the current SSB mixers of E1 by 2SB mixers of the type used already for the other three bands. The available frequency coverage may change slightly. In addition, we exchanged the local oscillator for the E330 band by a YIG LO to allow observations up to 370 GHz. ==== Nov-2011: 2SB mixers for E2 and E3 ==== In the first week of November 2011, we upgraded EMIR with '''dual sideband (2SB) mixers for bands E230 and E330'''. These mixers cov er 8 GHz of instantaneous bandwidth per sideband and per polarization, like E090. E150 is unchanged with single sideband (SSB) mixers and 4 GHz bandwidth per polarization. Below, comment (4) on Table 1, gives the '''new frequency ranges of E2 and E3'''. Figures below show the new bands, the new switch box scheme, and examples of '''band combinations''' which can be observed simultaneously. '''Commissioning has finished. First regular observations with EMIR have started again on 15-Nov.''' ==== Jul-2011: 32GHz IF-system, FTS backends ==== Since July 2011, we have made available a new '''32GHz IF system''' which includes '''24 fast fourier transform spectrometers (FTS)'''. This upgrade has duplicated the amount of instantaneous bandwidth available at the 30m telescope. 16 GHz of bandwidth can now be used instantaneously, in both polarisations. Eight cables of 4GHz width now carry the intermediate frequencies through the telescope cable spiral to the backend room. The full 32GHz of bandwidth are covered by 24 FTS working at '''200kHz''' resolution. This improves the available velocity resolution over large bandwidths by a factor of 10 compared to WILMA with its 2MHz resolution. It is now possible to observe at 0.6km/s resolution in the 3mm band allowing to resolve star forming clouds in the Milky Way and in nearby galaxies. The resolution of the 24 FTS can further be increased to '''50 kHz''', in which case only the '''inner 1.82GHz of the 4GHz EMIR bands''' are covered. The previous 4x4GHz system is still in use, and the additional 4x4GHz cables are connected to the outer 4GHz wide bands of EMIR 3mm channel, i.e. to E0UO and E0LO in both polarisations. All FTS units work either at 200 kHz or at 50 kHz. However it is not possible to set them individually to different resolutions. The new FTS can also be connected to the 2x9 HERA cables of 1GHz width, both at 200kHz or at 50kHz resolution. See also the call for proposals for the deadline in September 2011. See a brief report further below, and an [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Backends|overview of available backends, including the new broad band continuum (bbc) backend]] and [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Backends#IFdistributioninpreparationforendofJuly2011|the new IF distribution]]. === Sky frequencies === ||'''EMIR''' ||'''Fsky''' || '''mixer''' || '''polar-''' ||'''IF width''' || '''Trx''' || '''Gim''' || ||||||<style="TEXT-ALIGN: center">'''combinations''' ||'''Trx''' || '''[[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/TelescopeSystemStatus#EMIR|Status]]''' || '''Remark''' || || '''band''' || '''GHz''' || '''type''' || '''isation''' || '''GHz''' || '''K''' || '''dB''' || || '''E0/2''' || '''E1/3''' || '''E0/1''' || '''K''' || || || ||E0 || 73-117 ||2SB ||H/V ||8 || 50 || >10 || || X || || X || 65 || {{attachment:haken.gif}} || '''(1.1)''' || || || LSB: 73-97 (105) || || || || || || || || || || || || '''(1.2)''' || || || USB: 89-117 || || || || || || || || || || || || || ||E1 ||125-184 ||2SB ||H/V ||8 || 50 || >10 || || || X || X || 65 || {{attachment:haken.gif}} || '''(2)''' || || || LSB: 125-168 || || || || || || || || || || || || || || || USB: 141-184 || || || || || || || || || || || || || ||E2 ||202-274 ||2SB ||H/V ||8 || 80 || >10 || || X || || || 95 || {{attachment:haken.gif}} || '''(4, 5)''' || || || LSB: 202 (LO) - 263.5 (LI) || || || || || || || || || || || || || || || USB: 217 (UI) - 274 (UO) || || || || || || || || || || || || || ||E3 ||277-350 (375) ||2SB ||H/V ||8 || 80 || >10 || || || X || || 95 || {{attachment:haken.gif}} || '''(3, 4, 5, 6)''' || || || LSB: 277-335 || || || || || || || || || || || || || || || USB: 293-350 (375) || || || || || || || || || || || || || '''Table 1''': EMIR Frontend. '''Sky frequencies Fsky are given for the centers of the outer, respectively inner, 4GHz IF bands'''. Acronyms: 2SB - dual sideband mixers, SSB - single side band mixers, H/V -- horizontal and vertical polarizations, Trx is the SSB receiver temperature in single sideband observations, Gim is the image band rejection, LSB/USB are the lower and upper sidebands. Note that the receiver noise is somewhat increased when observing with two bands simultaneously due to the dichroic elements needed for these observations (see below for more details). '''General comment:''' Observers who intend to observe beyond the frequency ranges offered on the EMIR homepage should contact the Granada receiver group at least a week before the start of observations, even if these frequencies had previously been observed. This is to allow for time to check again if needed and inform the operators. <<BR>> '''(1.1)''' After the upgrade of E090 in November 2015, its frequency range has been extended down to 73 GHz. (The lower frequency limit of the local oscillator is 82.5GHz.) Note that the atmospheric transmission slowly degrades when going from 81 to 71GHz due to an atmospheric oxygen line at 60GHz. Thanks to the dominance of this line, the transmission over this frequency range hardly varies with water vapour and is therefore robust against changing weather conditions. The DCN 1-0 line at 72.41GHz and the DCO+ 1-0 line at 72.04 GHz are not officially covered by VESPA, nor the FTS at 50kHz. However, both lines can be observed with the FTS at 200kHz resolution, and with WILMA. <<BR>> '''(1.2)''' The LSB should be used for local oscillator frequencies of up to about 108GHz because at higher LO frequencies, the LSB shows rather poor image band rejections of upto -5dB. The USB should be used instead (cf. [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|plots of the gain ratios observed in the lab by D.Maier]]) <<BR>> '''(2)''' New 2SB E1 mixers have been installed in September 2013. The nominal RF frequency range of the E1 receiver is 127-179 GHz, which, referred to the centers of the outer 4 GHz bands, corresponds to 129-177 GHz. However, lab measurements done in the range '''124-184GHz''' (centers of outer bands; LO frequencies 134-174GHz) show a good performance of receiver temperatures and sideband ratios over this range (cf. [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|report by D.Maier (IRAM/Grenoble)]]), which we therefore offer to the astronomers. The receiver temperatures and gain ratios at the telescope will be roughly the same, but not exactly so, as the temperature environment and also some of the optics are different. The '''properties of the beam''' at the band edges are described in a [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|report by A.L.Fontana (IRAM/Grenoble)]]. Observations near the atmospheric water line at 183.31GHz require special care to correct for low atmospheric transmission. Observers requesting observations beyond the offered frequency range, i.e. beyond 184GHz, should contact the Granada receiver group as such observations require a good calibration strategy to measure the '''gain ratios''' (cf. a recent detection of !H2Cl+ at 189GHz by [[http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2013JPCA..11710018G|Gerin et al. 2013)]]. <<BR>> '''(3)''' As described in the commissioning report, the local oscillator of E3 shows instabilities at a few frequencies. If you as observer encounter such problems, please contact the operator and/or receiver engineer. Swapping the sideband may help. <<BR>> '''(4)''' In November 2011, EMIR bands E2 and E3 have been upgraded to full dual-polarisation, dual-sideband 8GHz each mixers. The frequency ranges have changed, in particular the overlap region between E2 and E3. Above, we give the new frequency ranges of E2 and E3. These are the centers of the outer bands which are '''reachable by all backends including VESPA'''. The FTS at 200kHz can reach frequencies which lie 2GHz further out. <<BR>> '''(5)''' E2 and E3 receiver temperatures have been measured at the telescope by SN in January 2012. For dual-band observations, we've added here 15K, as average number. However, observers should be aware that losses in the dichroics are frequency dependent as described further below. <<BR>> '''(6)''' In brackets is the frequency limit with the YIG local oscillator (LO), which extends beyond the nominal range offered by the Gunn LO. As of 4/2018, the YIG is installed. === Overview === The Eight MIxer Receiver EMIR was installed and commissioned at the 30m telescope in March through April 2009. EMIR replaced the single pixel heterodyne receivers A/B100, C/D150, A/B230, and C/D270. HERA, the bolometers, and the backends are unchanged. Since 2009, EMIR was upgraded to now offer an instantaneous bandwidth of up to 16 GHz in each of the two orthogonal linear polarizations for the 3, 2, 1.3 and 0.9mm atmospheric windows. In addition to the vast increase in bandwidth, the receiver offers considerably improved noise performance, a stable alignment between bands, and other practical advantages. The four EMIR bands are designated as E090, E150, E230, and E330 according to their approximate center frequencies in GHz. All bands are operated in dual-sideband, 2SB, mode with good imageband-rejections, where both sidebands are available for connection to backends. Furthermore, these bands are built in a technology that offers 8 GHz instantaneous bandwidth per sideband and polarization. Both polarizations of a given band will always be tuned to the same frequency as they share a single common local oscillator. The tuning ranges of the 4 bands, the typical receiver noise temperatures, and other parameters are listed in Tab.1. EMIR provides for the first time in the history of the 30m telescope a permanently available high sensitivity E330 band, opening this atmospheric window for regular use under good weather conditions. See the commissioning report below. [[#beginOfPage|Back to top]] {{attachment:atm-iram30mv4.png| Atmospheric transmission | width=750}} <<BR>> '''Figure 1''': Atmospheric transmission between 60 and 400GHz for two precipitable water vapors, modeled with the ATM model. The EMIR bands are marked together with the frequencies of a few important molecular transitions. === EMIR bands === {{attachment:EMIRbands_26092013.png| EMIR bands | width=750}}<<BR>> '''Figure 2:''' Overview of EMIR band combinations and frequencies which are available after the EMIR upgrade and commissioning in September/October-2013. Central frequencies of the (sub-)bands refer to VESPA, and the band edge frequencies are given for WILMA and the FTS backends in the two resolution presets. Frequency edges are taken from the list provided by G.Paubert on the [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Backends|backends page]]. === EMIR band combinations === EMIR has four different bands covering the four main atmospheric windows in the millimetre range: E090, E150, E230 and E330. Dual band observation is possible but only the E0/E1, E0/E2 and E1/E3 band combinations are allowed by the receiver optics. Each of the four bands (E0, E1, E2, and E3) have four IF outputs: 2 polarizations (H,V) and 2 sidebands (L,U), each of them is 8 GHz wide. The 8GHz wide IF outputs are split in two blocks, 4 GHz wide each, denoted by I and O (inner and outer) and sent to the spectrometers by the use of in total 8 coaxial cables. This means that a total of 32GHz of bandwidth are transferred to the spectrometers. In the future, we plan to upgrade the IF-system and backends to allow for 64GHz of total bandwidth, the maximum EMIR offers. The FTS backends can be connected to all 8 cables, while the old backends VESPA and WILMA can only be connected to IF cables 1-4. When designing the new switch box, we assumed that most will want to use both polarisations simultaneously. Aside from improving the signal-to-noise ratios, this observing mode allows for easy checks of the relative calibration. Commissioned EMIR band combinations or setups: 1. '''One band only''': 1. '''E0 LI+LO, UI+UO''' (dual-pol, 16GHz bandwidth) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. '''E1 LI+LO, UI+UO''' (dual-pol, 16GHz bandwidth) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. '''E2 LI+LO, UI+UO''' (dual-pol, 16GHz bandwidth) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. '''E3 LI+LO, UI+UO''' (dual-pol, 16GHz bandwidth) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. '''E2 LO+UO ''' (special setup to use only IF bands 1-4, allowing to connect VESPA e.g. for polarimetry) 1. '''E0/E2''': 1. '''E0: UI+UO, E2: UI+UO''' (dual-pol, 16GHz, e.g. 12CO, 13CO 1-0, 12CO 2-1) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. '''E0: LI+LO, E2: LI+LO''' (dual-pol, 16GHz, e.g. HCN, HCO+ 1-0, 13CO 2-1) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. '''E0H: LO+LI+UI+UO, E2V: LO+LI+UI+UO''' (single-pol, 32GHz, H<->V) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. Special setups (not tested after the upgrade in Sep-2013): 1. E0VUO (12CO 1-0), E2VUI, E2HUI (12CO 2-1), E2HLI (13CO & C18O 2-1) [only 4 IF-cables used] 1. E2HLI, E2HUI, E0VUI (or any other E0V band) (12CO & 13CO 2-1 + 3mm) [single-pol] 1. E2UO, E2UI, E0UO, E0UI (using IF-cables 1-4, 12-Jan-2012) 1. E0LOH, E0LOV, E0UIH, E2LIV (HCN/HCO+ in dual-pol, 13CO 1-0 & 2-1 in single-pol; seems possible but has not been tested) 1. '''E1/E3''': 1. '''E1: UI+UO, E3: UI+UO''' (dual-pol, 16GHz) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. '''E1: LI+LO, E3: LI+LO''' (dual-pol, 16GHz) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. '''E1H: LO+LI+UI+UO, E3V: LO+LI+UI+UO''' (single-pol, 32GHz) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. Obsolete setups after Sep-2013: 1. E1V+E1H+E3VL+E3HL 1. E1LI, E3LI, E3LO (dual-pol) 1. E1UI, E3LI, E3VLO (dual-pol) 1. E1UI, E3UI [after the switchbox upgrade in Oct-12] 1. E1LI, E3UI [after the switchbox upgrade in Oct-12] 1. '''E0/E1''': 1. '''E0: UI+UO, E1: UI+UO''' (dual-pol, 16GHz) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. '''E0: LI+LO, E1: LI+LO''' (dual-pol, 16GHz) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. '''E0H: LO+LI+UI+UO, E1V: LO+LI+UI+UO''' (single-pol, 32GHz, H<->V) {{attachment:haken.gif}} 1. Obsolete setups after Sep-2013: 1. Together with E1, only the lower bands of E0 can be observed in dual-pol. Inner and outer bands can be observed simultaneously for E0. Important application: CS 2-1, 3-2. 1. EOLI, E0LO, E1LI (dual-pol) 1. E0LI, E0LO, E1UI (dual-pol) 1. E0UI, E1UI [after the switchbox upgrade in Oct-12] 1. E0UI, E1LI [after the switchbox upgrade in Oct-12] 1. E0LOH, E0LIV, E0UIH, E1LIV ! special setup, as only one polarisation is used. Allows to observe three transitions of NH2D simultaneously. Setups which are '''not''' possible: 1. 3mm: UI+UO, 1mm: LI+UI (12CO, 13CO 1-0 & 2-1) ! Only a maximum of 4 inner cables can be selected. 1. E0 LI,UI + E2 LI,UI ! Only a maximum of 4 inner bands can be selected. In general, when connecting to E2 LI+UI with both polarisations, none of the inputs of E0 are accessible. 1. E0 LO UO + E2 LO LI 1. 50kHz FTS: C18O, 13CO, 12CO 1-0 simultaneously. These lines lie 5.49GHz apart, while the outer edges of the FTS 50kHz units in the inner and outer band of EMIR lie 5.42GHz apart. The inner edges lie 1.78GHz apart. However, it is no problem to observe these lines simultaneously with 200kHz resolution. 1. E0 alone with only two If cables attached, e.g. horizontal LI vertical LI, results in corrupted FTS raw data (imbfits files that mira can not read and result in a Segmentation fault). A Workaround is to attach 4 cables, e.g. horizontal UI+LI and vertical UI+LI. More details on the selection rules and a sketch of the switch box, are given here: SwitchBoxDetails. See also the [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#EMIRpaperandcommissioningReports|commissioning report]] below. [[#beginOfPage|Back to top]] === Focal plane geometry === The four bands will be combined in only two possible beams (left and the right beams when looking to the cryostat front face). The left and right beams are offset by about 90" on the sky. See the [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/TelescopeSystemStatus#PointingandAlignment|telescope status page]] for the present Nasmyth offsets (cf. EMIR Commissioning report below). Observations are carried out with either of the two beams. Simultaneous observations with both beams are at present not supported. === Selection of EMIR bands (Dichroics) === {{attachment:emir.png}} Before reaching the Nasmyth mirrors, the four beams of the EMIR bands pass through warm optics that contains switchable mirrors and dichroic elements for redirection of the beams towards calibration loads and for combining beams. In its simplest mode, the warm optics unit selects one single EMIR band for observation. This mode avoids the use of the slightly lossy dichroic elements and therefore offers the best receiver noise temperatures. Three dichroic mirrors are available for combining either the E090 and E150 beams, or the E090 and E230 beams, or the E150 and E330 beams (Table 1). The combination of bands is not polarization selective, i.e. the combined bands will stay dual polarization. The loss of these dichroics increases however the receiver temperatures by, in general, only 10 - 15 K. The losses of E2 (due to the use of the dichroic) are higher than 10% for frequencies above ~258GHz and below ~202GHz (cf. Table 2). The polarization angle of the dichroic was chosen to minimize the losses for 231GHz. The observer is therefore adviced to carefully evaluate whether an observation involving two different bands is more efficiently made in parallel or in series. Simultaneous observations of e.g. HCO+ at 89.7 and 266.5GHz with E0 and E2, are possible after the replacement of the E0/E2 dichroic in September 2016. The dichroics are needed for dual-band observations with EMIR. The following table shows the losses of the dichroics, based on a separate mixer and dichroic characterization done in the receiver lab by Anne-Laure Fontana in Feb 09. '''Table 2: Performance of dichroics (February 2009, Report of Anne Laure)''': ||||||||<style="TEXT-ALIGN: center"> E0/E2 ||||||||<style="TEXT-ALIGN: center"> E0/E1 ||||||||<style="TEXT-ALIGN: center"> E1/E3 || || E0 || E0 || E2 || E2 || E0 || E0 || E1 || E1 || E1 || E1 || E3 || E3 || || GHz || % || GHz || % || GHz || % || GHz || % || GHz || % || GHz || % || || 84-108 || 2.5 || 202 || 10 || 84 || 4 || 129 || 5 || 129-138 || 2.5 || 261-357 || <2.5 || || 116 || <2 || 213 || 5 || 92 || 3.2 || 138-156 || 1 || 147 || 4.5 || 369 || 7 || || || || 225 || 3 || 100-110 || 5 || 168 || 2 || 156 || 3.5 || || || || || || 231 || 2 || 110-115 || ~10 || 171 || 2 || 174 || 2.5 || || || || || || 243 || 5 || || || 174 || 2 || 180 || ~5 || || || || || || 255 || 5 || || || || || || || || || || || || 258 || 10(1) || || || || || || || || || || || || 267 || 50(1) || || || || || || || || || Each percent of losses, increases the receiver temperature by about 4K. <<BR>> (1) '''Note that these values have much improved after the replacement of the dichroic D13 in September 2016!''' [[#beginOfPage|Back to top]] === IF Distribution === An overview of the current disbribution of intermediate frequencies (IF) is given [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Backends#CurrentstatusofIFdistribution|here]]. === Connection to backends === Eight output channels are sent via the IF cables to the [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Backends|backends at the IRAM 30m telescope]]: * the Fast Fourier Transform Spectrometers (FTS) handle input from all 4 cables. * The other backends take as input the (old) IF cables 1-4 only: Three backend processors have been build to feed the new 4 GHz wide IF channels to the existing backends: * The '''WILMA processor''' rearranges the four incoming 4 GHz wide IF channels into 16 channels of 1 GHz width which can be processed by 16 WILMA autocorrelator units. Since each unit provides 512 spectral channels of 2 MHz, sufficient backend power is available at low spectral resolution for full coverage of the 4x4GHz bottleneck. * The '''narrow backend processor''' prepares the 4 incoming IF channels for input into '''VESPA'''. Only the central part of the 4 GHz IF channels is accessible to these backends. Inside this central part (1 GHz for the filterbank and 640 MHz for VESPA), these backends can be configured as before. The VLBI terminal is also fed from this processor. * When planning to observe several interstellar lines simultaneously with EMIR, it is sometimes difficult to check whether this is possible with the FTS at 50kHz resolution and VESPA. GILDAS versions of July 2016 and younger, include a powerful tool, ASTRO\EMIR, to prepare the detailed frequency setups. This supersedes the following small GREG script, to help finding a local oscillator frequency to allow for simultaneous observations of several lines with both sidebands of one of the four EMIR receivers. The [[attachment:specsetupv3.greg|greg-script]] plots the frequency coverage of the FTS at 200 and 50kHz, and the 500MHz bandwidth of VESPA, together with a set of lines to be observed, using a given LO frequency: {{attachment:specsetup.png|Example plot}} <<BR>> '''Figure 3:''' Frequency coverages of the various backends. [[#beginOfPage|Back to top]] === Temperature calibration === EMIR comes with a new calibration system. The external warm optics provides ambient temperature loads and mirrors reflecting the beams back into the 15 K stage of the cryostat. This system is expected to be very reliable and constant over time. Absolute calibration accuracy will be better than 10% with EMIR when all details are well settled. All bands have tunerless sideband separation mixers, allowing simultaneous observations of both sidebands in separate IF bands. These mixers have been characterized in the laboratory for their image rejection and are expected to have the same performance on site (>13dB). [[#beginOfPage|Back to top]] === Correct frequency scales over upto 24 GHz of bandwidth === It is common practice at radio observatories to correct the frequency of an observation for the strongly time variable velocity of the Observatory with respect to the solar system barycenter. This guarantees that lines observed near the Doppler-tracked frequency, usually the band center, always have the correct barycentric velocity, independent of the time of observation. At the 30m, the local oscillator and its synthesizers are constantly adjusted during observations to track the changing Doppler factor for one spectral line with its rest frequency. This causes a slight shift of lines observed simultaneously at a diff erent frequency. This shift is proportional to the frequency diff erence and the Doppler factor. CLASS corrects for this shift by adapting the spectral resolution. As the report below describes, these shifts correspond to time variable changes of the frequency resolution. Co-adding or averaging spectra taken at different times, may then lead to a broadening of the effective frequency resolution. [[attachment:buchbender-03aug11-reportShiftTest_ver1-4.pdf|Accurate line center frequencies]]: Report of 03-Aug-2011 by Buchbender, Kramer et al.. Two bugs in mira and class caused frequency shifts and have been corrected for. The new versions of mira and class were installed at the 30m on 16-Aug-2011. [[#beginOfPage|Back to top]] === PaKo user interface === The new default !PaKo version supports the upgraded E2 and E3 mixers and the enhanced IF switch box. See the current [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/documents/ncs30mPako/Current/PDF/pako.pdf|PaKo manual]]. Please contact your astronomer-of-duty to help you prepare scripts or in case of any questions. === EMIR Observations Time Estimator === * [[http://iram-institute.org/EN/content-page.php?ContentID=150&rub=7&srub=55&ssrub=150&sssrub=0&ssssrub=0|EMIR observing time estimator]] === Telescope efficiencies === * [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Iram30mEfficiencies|Telescope Efficiencies]] === Alignment === The current alignment between polarisations and between EMIR bands is given [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/TelescopeSystemStatus#EMIR-1|here]]. === Observatory status === * [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/TelescopeSystemStatus|Telescope Status Page]] === Reports and publications === * [[attachment:e230-lo-filter.pdf|Suppression of E230 ghost lines after installation of an LO filter]], 25-Apr-2017, Marka, Navarro, John. * [[attachment:EMIR-D13-2016.pdf|EMIR Upgrade of Dichroic D13 in 2016 – Tests in NCS at PV]], H. Ungerechts et al.. 1-Feb-2017 * [[attachment:e230-ghost-v2.pdf|Report on E230 ghost lines from unwanted 7th harmonic of the LO]], 20-Jan-2017, Marka and Navarro. * [[attachment:sievers-01apr2016-E090-OMT-XPOL-v3.pdf|Commissioning Report on XPOL E090 with OMT]], 1-Apr-2016 by A. Sievers. * [[attachment:e090-ghost-mar2016.pdf|Report on suppression of E090 ghost lines after installation of an LO filter]], 31-March-2016, Navarro and Marka. * [[attachment:report-e150-ghost-mar2016.pdf|Report on E150 ghost lines from unwanted 5th harmonic of the LO]], 16-March-2016, Marka and Navarro. * [[attachment:report-e0e1upgrades-15dec2015-v1.1.pdf|Commissioning of the upgraded E090 and E150 bands]] (15-Dec-2015, C.Marka and C.Kramer) * [[attachment:sievers-19oct2015-newOptics-XPOL-v2.pdf|Commissioning Report on XPOL using the New Optics]], 19-Oct-2015 by Sievers et al.. For more information on XPOL, see [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/PolarimetryforAstronomers|here]]. * [[attachment:new-optics-commissioning-apr2015-v0.9.4.pdf|Commissioning Report on the New Optics]], 29-May-2015 by Ungerechts et al. * [[attachment:gainratios_v3.pdf|Report on E150 image band rejections]], 30-March-2015 by Marka et al. * [[attachment:ghosts-v1.2.pdf|Report on suppression of E150 ghost lines after installation of an LO filter]], 26-March-2015 by Sievers et al. * [[attachment:emir-ghosts-v1.2.pdf|Report on EMIR ghost lines (unwanted harmonics of the local oscillators]], 21-August-2014 by Kramer, Navarrini, Navarro, John, Cernicharo * [[attachment:fontana-jul2014-122-186GHz-EMIRB2-optics.pdf|Report on E1 optics in the 122 - 186 GHz range]]: performance at the band edges, July 2014 by Anne Laure Fontana (IRAM/Grenoble) * [[attachment:maier-2014-lab-measurements-EMIR-mixers.pdf|Report on Lab measurements of EMIR receivers]]: receiver temperatures and image band rejections, June 2014 by Doris Maier (IRAM/Grenoble) * '''The EMIR Multi-band mm-Wave Receiver''' for the IRAM 30m Telescope, [[http://esoads.eso.org/abs/2012A%26A...538A..89C|Carter, Lazareff et al. 2012]] (A&A, 538, 89) * The current beam pattern of the 30m telescope is described in a new report, based on EMIR observations covering the entire frequency range between 86 and 345GHz. The main beam efficiencies have considerably improved relative to the values compiled in Greve et al. (1998). See [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Iram30mEfficiencies|here]] or [[http://www.iram-institute.org/EN/content-page-161-7-66-161-0-0.html|here]]. * Commissioning Reports: * Bands 1-3: [[attachment:EmirCommissioningReportVers1.1.pdf]] (4/2009) * Band 4: [[attachment:emir-e3-com-report-05apr2010.pdf]] (4/2010) * Polarimetry (Bands 1&3) [[attachment:wiesemeyer-thum-xpol-report-10aug2010.pdf]] (8/2010) * Upgrade to 32GHz IF system [[attachment:kramer-aug2011-32ghz-newsletter.pdf]] (7/2011) * Upgrade of E2 and E3 mixers (Nov 2011) * [[attachment:emir-nov11-com-report-v1.0.pdf]] Report on spectral line commissioning observations by Kramer et al. * [[attachment:e2-09apr2012.pdf]] Report on E230 issues encountered till 23-February-2012. [[#beginOfPage|Back to top]] === Historic news === * E090: Spectral sidelobes have not been detected anymore in E090H, after swapping the mixer bias boxes of E090 and E330 on 22-January. E330 has also been checked and shows no such problems. These "spectral sidelobes" had been an issue after the upgrade of E090 in November last year. <27-Jan-2016> * E090: The following issue has been resolved by installing a filter in the local oscillator path on 22-Mar-2016 (see a short report [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|here]]). Before that date, the unwanted 3rd harmonic of the Gunn oscillator of E090 local oscillator had not been sufficiently suppressed. It had leaked through to the mixers and lead to detection of strong lines stemming from outside the observed band. * The new receiver cabin optics has been installed and optically aligned: To prepare for NIKA-2 and future heterodyne array cameras new, larger mirrors M3 and M4 have been installed, together with new mounts. EMIR mirrors M5, M6, and M7 also had to be adapted, and HERA was moved a few cm to its new position. After a successful optical alignment, astronomical commissioning using all bands of EMIR went well without major issues. Commissioning of HERA also went well. (cf. [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|A report is available online]]). <29-May-2015> The commissioning report on polarimetry with EMIR XPOL is available [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|here]]. <19-Oct-2015> * Image band rejections of E150 have degraded since installation of the new dual-sideband (2SB) mixers in September 2013, in particular for the Vertical Polarisation. The average rejection is now about -7dB (factor 5) instead of -13dB (factor 20). This finding is currently being discussed with the receiver groups in Granada and Grenoble. (cf. [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|report of 30-March-2015]]). The gain ratio depends to some degree on the LO and mixer settings as this report and also the lab report shows. As the antenna temperature is proportional to (1+!GainRatio), observers interested in a high calibration accuracy may want to measure the gain ratio as function of frequency for their particular observational setup using both sidebands simultaneously, e.g. on a line calibrator source. * To suppress any "ghost" lines in E150, a filter of the local oscillator was installed on 2-Dec-2014. The outer edges of E1 can still be reached and E1 has been used since then without problems. [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|The filter works very well (cf. report of 25-March-2015)]]. * E330 YIG LO has been installed (LO-range 283-365GHz) (see below). <Oct-2014> * Observers who intend to observe beyond the frequency ranges offered on the EMIR homepage should contact the Granada receiver group at least a week before the start of observations, even if these frequencies had previously been observed. This is to allow for time to check again if needed and inform the operators. * A [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|report on gain ratios and receiver temperatures from lab measurements of the installed EMIR mixers for all four bands]] has been prepared by D.Maier (IRAM/Grenoble). See also the comment 1.2. in [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Sky_frequencies|Table 1]] on the recommended LSB frequency range of E090. * '''E150 frequency range:''' Information on the E150 frequency range has been updated (cf. [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Sky_frequencies|Table 1]]). See also a [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|report]] by A.L.Fontana (IRAM/Grenoble) on the system performance of E150 at its band edges. * '''EMIR Ghost Lines:''' The EMIR local oscillators (LOs) do create harmonics of its Gunn oscillators, which are mixed in the sideband separating mixers, and then down converted into the IF (intermediate frequency) band. The LOs do, however, also create unwanted harmonics which may not be sufficiently suppressed, leak through, and pump the mixers. This may lead to detections of ghost lines stemming from much higher frequencies, far outside the nominal frequency range, polluting the observed spectra. Such lines have recently been identified in frequency surveys of IRC+10216: in one example, a ghost line showed-up at 129GHz in the E150 band, which does however stem from a line at 196GHz. With the large bandwidths provided by EMIR, and with deep frequency surveys on '''bright Galactic star forming regions like Orion''' showing a large dynamic range of line temperatures, addressing these ghost lines becomes important. A [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Reports_and_publications|report]] has been prepared to inform the observers of the current status of this issue, describe the origin of the harmonics, give observational examples showing also how to detect ghosts, and describe counter measures which are currently being prepared by the IRAM frontend groups. <21-August-2014 CK> * The script to check the possibility to observe several lines with one of the EMIR receivers and the present set of backends, has been updated now providing more information on the frequency distance to the edges of the bands and on possible sky frequencies for pako. See [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/EmirforAstronomers#Connection_to_backends|below "Connection to Backends"]]. * The current beam pattern of the 30m telescope is described in a new report, based on EMIR observations covering the entire frequency range between 86 and 345GHz. The main beam efficiencies have considerably improved relative to the values compiled in Greve et al. (1998). See [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Iram30mEfficiencies|here]] or [[http://www.iram-institute.org/EN/content-page-161-7-66-161-0-0.html|here]]. * The local oscillator for EMIR band 4, E330, had to be sent to Grenoble for repair. We re-installed the Gunn LO with its upper frequency limit of 358 GHz. (12-February-2014) * News on the upgrade of E150 and E330 in Sep-2013: * Installation of the new 2SB mixers for E150 and of the new YIG LO for E330, went well. New versions of pako and of the software controlling the IF switchbox have been tested and implemented. A commissioning report is in preparation. * E1 frequency survey between 125 and 186GHz went well. Same for tests of the basic setups of the IF switchbox. All successfully tested setups are marked with a {{attachment:haken.gif}} in the listing of setups below. * E3 has been tested at local oscillator frequencies between 300 and 360 GHz. * Antenna temperatures of E1 upper sideband (USB) observations at sky frequencies between 144 and 147 GHz have been found to be a factor ~2 lower than lower sideband (LSB) spectra due to a wrong tuning table leading to a poor image band rejection. The tuning table was wrong since the installation of EMIR in 4/2009, but has been corrected now. We have found no indications for such problems outside the above frequency range. <9-Jan-2013 CK> * We have implemented a small upgrade of the IF switchbox which now allows simultaneous observations of E3 in USB together with E1, and of E0 USB together with E1. The former setup will be helpful for high frequency E3 observations together with pointings using E1. All previously possible IF setups stay available after this upgrade. See switch box details below. <28-Oct-2012 CK> * The local oscillator for E330 has been refurbished such that EMIR can now reach sky frequencies up to 358 GHz, giving access to the 4-3 transitions of HCN and HCO+ under excellent weather conditions. <30-Jul-2012 CK> * A dedicated paper on the working of EMIR and first results has been published by [[http://esoads.eso.org/abs/2012A%26A...538A..89C|Carter, Lazareff et al. 2012]] (A&A, 538, 89). * Observers have been informed on 26-Apr-2012 on problems for some frequencies with E230 between 15-Nov-2011 and 23-Feb-2011 when this band showed excess noise, spurious signals, and calibration problems. Improving on the tuning parameters solved this. * The E0/E1 alignment is better than 1", after repositioning the EMIR caroussel no. 2 on 29-Nov-2011, and later replacing its position sensor. * The main EMIR band setups possible after the upgrade of E2 and E3, and of the IF switch-box, have been successfully commissioned in November 2011. Possible EMIR band combinations are detailed below. ''This page is maintained by C.Kramer. Any comments are welcome.'' |
Contents
-
EMIR Users Guide
- News (last update: 25-Apr-2017, CM)
- Upgrades
- Sky frequencies
- Overview
- EMIR bands
- EMIR band combinations
- Focal plane geometry
- Selection of EMIR bands (Dichroics)
- IF Distribution
- Connection to backends
- Temperature calibration
- Correct frequency scales over upto 24 GHz of bandwidth
- PaKo user interface
- EMIR Observations Time Estimator
- Telescope efficiencies
- Alignment
- Observatory status
- Reports and publications
- Historic news
EMIR Users Guide
News (last update: 25-Apr-2017, CM)
A filter was installed in the E230 band on 14-Feb-2017, suppressing unwanted harmonics of the LO (see here), which had been generating spurious lines. Other (weak) harmonics created later in the chain cannot be suppressed by the current filter. <CM, 25-Apr-2017>
After an exchange of compressors, the mixer temperature of EMIR is back to 3.7K. <24-Apr-2017>
We have received reports of spurious lines in the E230 band of EMIR. Two independent reasons have been identified: (1) change of mixer biasing because of slightly increased physical temperatures (about 4.2K) after exchange of cold head last year. (2) Unwanted harmonics of the fundamental frequency of the local oscillator (see report of Jan. 2017). To tackle item (1), we plan to update the tuning table. And for item (2), we plan to install a filter, as we had done in the past for the local oscillator of E090 and E150. <18-Jan-2017>
Since 17-January 2017, the dichroic mirror D24 is kept in place not only for E1/E3 observations, but also when observing only with E330. See the report by H.Ungerechts of 1-February.
In mid February 2017 (date changed), we plan to change the online data processing from MIRA to MRT-CAL for most of the data. Exceptions are XPOL/EMIR data, and continuum data (e.g. pointing, focus, skydips). There will be a few subtle changes. See Tutorials on the GILDAS home page. MRT-CAL is alreay included into the GILDAS package, and, for the foreseeable future, MIRA will stay available.
E150: On 9-August 2016, a filter was installed at the output of the E1 local oscillator box in order to suppress generated harmonics of the Gunn fundamental frequency. Lop1 attenuator values were also modified in the LO tuning table in order to compensate for the extra power loss introduced by this filter/waveguide combination. Gunn frequencies @ (67.75, 74.0, 80.0, 81.0, 87.0) GHz was checked and sufficient power was obtained to pump the mixers. (Total LO 135.5, 148.0, 160.0, 162.0, 174.0)GHz. (DJ 10-Aug) The spurious line which had been detected in Dec 2015 ( Marka & Kramer, Dec-2015) is not seen anymore. The rejection is better than -34dB. (SN 11-Aug).
EMIR frequency setups can now be prepared using a new set of commands in ASTRO\PICO (GILDAS versions of July 2016 or younger). These take into account the available frequency limits, band combinations, and spectrometers, and plot the covered frequency ranges together with known spectral lines, taking into account source velocities or redshifts. This new functionality is still under development and is likely to be upgraded in the future. Examples are given here, but see also the online help.
After the upgrade of the E0 and E1 bands in November 2015, the alignment between bands has somewhat degraded, as also the relative focus offsets (Marka & Kramer, Dec-2015).
Spectroscopic polarimetry observations in bands E0 and E1 show an increase of the instrumental circular polarisation for reasons not yet understood (see here).
For older news check here.
Upgrades
Sep-2016: New dichroic for E0/E2 dual-band operation
During heavy maintenance end of September 2016, we have installed a new dichroic mirror for E0/E2 dual-band operation, which is strongly improving receiver noise temperatures in dual-band observations at the high frequency end of E230 above 240GHz, compared to the numbers of 2009 given in Table 2 below. In particular, this will allow efficient observations simultaneously of the 1-0 and 3-2 transitions of HCN, HNC, HCO+. See the report by H.Ungerechts of 1-February-2017.
Dec-2015: New 2SB mixers for E0 and E1
EMIR bands E090 and E150 have been upgraded end of November 2015. Mixers have been replaced by NOEMA-type mixers. For E090, an ortho-mode transducer with one horn only, splits both polarisations. The frequency range of E090 has been extended down to almost 70GHz (see details below). Commissioning has shown that in general the upgrade went well. See further comments in the news section.
Sep-2013: 2SB mixers for E1
We exchanged the current SSB mixers of E1 by 2SB mixers of the type used already for the other three bands. The available frequency coverage may change slightly. In addition, we exchanged the local oscillator for the E330 band by a YIG LO to allow observations up to 370 GHz.
Nov-2011: 2SB mixers for E2 and E3
In the first week of November 2011, we upgraded EMIR with dual sideband (2SB) mixers for bands E230 and E330. These mixers cov er 8 GHz of instantaneous bandwidth per sideband and per polarization, like E090. E150 is unchanged with single sideband (SSB) mixers and 4 GHz bandwidth per polarization. Below, comment (4) on Table 1, gives the new frequency ranges of E2 and E3. Figures below show the new bands, the new switch box scheme, and examples of band combinations which can be observed simultaneously. Commissioning has finished. First regular observations with EMIR have started again on 15-Nov.
Jul-2011: 32GHz IF-system, FTS backends
Since July 2011, we have made available a new 32GHz IF system which includes 24 fast fourier transform spectrometers (FTS). This upgrade has duplicated the amount of instantaneous bandwidth available at the 30m telescope. 16 GHz of bandwidth can now be used instantaneously, in both polarisations. Eight cables of 4GHz width now carry the intermediate frequencies through the telescope cable spiral to the backend room. The full 32GHz of bandwidth are covered by 24 FTS working at 200kHz resolution. This improves the available velocity resolution over large bandwidths by a factor of 10 compared to WILMA with its 2MHz resolution. It is now possible to observe at 0.6km/s resolution in the 3mm band allowing to resolve star forming clouds in the Milky Way and in nearby galaxies. The resolution of the 24 FTS can further be increased to 50 kHz, in which case only the inner 1.82GHz of the 4GHz EMIR bands are covered. The previous 4x4GHz system is still in use, and the additional 4x4GHz cables are connected to the outer 4GHz wide bands of EMIR 3mm channel, i.e. to E0UO and E0LO in both polarisations. All FTS units work either at 200 kHz or at 50 kHz. However it is not possible to set them individually to different resolutions. The new FTS can also be connected to the 2x9 HERA cables of 1GHz width, both at 200kHz or at 50kHz resolution. See also the call for proposals for the deadline in September 2011.
See a brief report further below, and an overview of available backends, including the new broad band continuum (bbc) backend and the new IF distribution.
Sky frequencies
EMIR |
Fsky |
mixer |
polar- |
IF width |
Trx |
Gim |
|
combinations |
Trx |
Remark |
|||
band |
GHz |
type |
isation |
GHz |
K |
dB |
|
E0/2 |
E1/3 |
E0/1 |
K |
|
|
E0 |
73-117 |
2SB |
H/V |
8 |
50 |
>10 |
|
X |
|
X |
65 |
|
(1.1) |
|
LSB: 73-97 (105) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(1.2) |
|
USB: 89-117 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E1 |
125-184 |
2SB |
H/V |
8 |
50 |
>10 |
|
|
X |
X |
65 |
|
(2) |
|
LSB: 125-168 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
USB: 141-184 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E2 |
202-274 |
2SB |
H/V |
8 |
80 |
>10 |
|
X |
|
|
95 |
|
(4, 5) |
|
LSB: 202 (LO) - 263.5 (LI) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
USB: 217 (UI) - 274 (UO) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E3 |
277-350 (375) |
2SB |
H/V |
8 |
80 |
>10 |
|
|
X |
|
95 |
|
(3, 4, 5, 6) |
|
LSB: 277-335 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
USB: 293-350 (375) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Table 1: EMIR Frontend. Sky frequencies Fsky are given for the centers of the outer, respectively inner, 4GHz IF bands. Acronyms: 2SB - dual sideband mixers, SSB - single side band mixers, H/V -- horizontal and vertical polarizations, Trx is the SSB receiver temperature in single sideband observations, Gim is the image band rejection, LSB/USB are the lower and upper sidebands. Note that the receiver noise is somewhat increased when observing with two bands simultaneously due to the dichroic elements needed for these observations (see below for more details).
General comment: Observers who intend to observe beyond the frequency ranges offered on the EMIR homepage should contact the Granada receiver group at least a week before the start of observations, even if these frequencies had previously been observed. This is to allow for time to check again if needed and inform the operators.
(1.1) After the upgrade of E090 in November 2015, its frequency range has been extended down to 73 GHz. (The lower frequency limit of the local oscillator is 82.5GHz.) Note that the atmospheric transmission slowly degrades when going from 81 to 71GHz due to an atmospheric oxygen line at 60GHz. Thanks to the dominance of this line, the transmission over this frequency range hardly varies with water vapour and is therefore robust against changing weather conditions. The DCN 1-0 line at 72.41GHz and the DCO+ 1-0 line at 72.04 GHz are not officially covered by VESPA, nor the FTS at 50kHz. However, both lines can be observed with the FTS at 200kHz resolution, and with WILMA.
(1.2) The LSB should be used for local oscillator frequencies of up to about 108GHz because at higher LO frequencies, the LSB shows rather poor image band rejections of upto -5dB. The USB should be used instead (cf. plots of the gain ratios observed in the lab by D.Maier)
(2) New 2SB E1 mixers have been installed in September 2013. The nominal RF frequency range of the E1 receiver is 127-179 GHz, which, referred to the centers of the outer 4 GHz bands, corresponds to 129-177 GHz. However, lab measurements done in the range 124-184GHz (centers of outer bands; LO frequencies 134-174GHz) show a good performance of receiver temperatures and sideband ratios over this range (cf. report by D.Maier (IRAM/Grenoble)), which we therefore offer to the astronomers. The receiver temperatures and gain ratios at the telescope will be roughly the same, but not exactly so, as the temperature environment and also some of the optics are different. The properties of the beam at the band edges are described in a report by A.L.Fontana (IRAM/Grenoble). Observations near the atmospheric water line at 183.31GHz require special care to correct for low atmospheric transmission. Observers requesting observations beyond the offered frequency range, i.e. beyond 184GHz, should contact the Granada receiver group as such observations require a good calibration strategy to measure the gain ratios (cf. a recent detection of H2Cl+ at 189GHz by Gerin et al. 2013).
(3) As described in the commissioning report, the local oscillator of E3 shows instabilities at a few frequencies. If you as observer encounter such problems, please contact the operator and/or receiver engineer. Swapping the sideband may help.
(4) In November 2011, EMIR bands E2 and E3 have been upgraded to full dual-polarisation, dual-sideband 8GHz each mixers. The frequency ranges have changed, in particular the overlap region between E2 and E3. Above, we give the new frequency ranges of E2 and E3. These are the centers of the outer bands which are reachable by all backends including VESPA. The FTS at 200kHz can reach frequencies which lie 2GHz further out.
(5) E2 and E3 receiver temperatures have been measured at the telescope by SN in January 2012. For dual-band observations, we've added here 15K, as average number. However, observers should be aware that losses in the dichroics are frequency dependent as described further below.
(6) In brackets is the frequency limit with the YIG local oscillator (LO), which extends beyond the nominal range offered by the Gunn LO. As of 4/2018, the YIG is installed.
Overview
The Eight MIxer Receiver EMIR was installed and commissioned at the 30m telescope in March through April 2009. EMIR replaced the single pixel heterodyne receivers A/B100, C/D150, A/B230, and C/D270. HERA, the bolometers, and the backends are unchanged. Since 2009, EMIR was upgraded to now offer an instantaneous bandwidth of up to 16 GHz in each of the two orthogonal linear polarizations for the 3, 2, 1.3 and 0.9mm atmospheric windows. In addition to the vast increase in bandwidth, the receiver offers considerably improved noise performance, a stable alignment between bands, and other practical advantages.
The four EMIR bands are designated as E090, E150, E230, and E330 according to their approximate center frequencies in GHz. All bands are operated in dual-sideband, 2SB, mode with good imageband-rejections, where both sidebands are available for connection to backends. Furthermore, these bands are built in a technology that offers 8 GHz instantaneous bandwidth per sideband and polarization. Both polarizations of a given band will always be tuned to the same frequency as they share a single common local oscillator. The tuning ranges of the 4 bands, the typical receiver noise temperatures, and other parameters are listed in Tab.1.
EMIR provides for the first time in the history of the 30m telescope a permanently available high sensitivity E330 band, opening this atmospheric window for regular use under good weather conditions. See the commissioning report below.
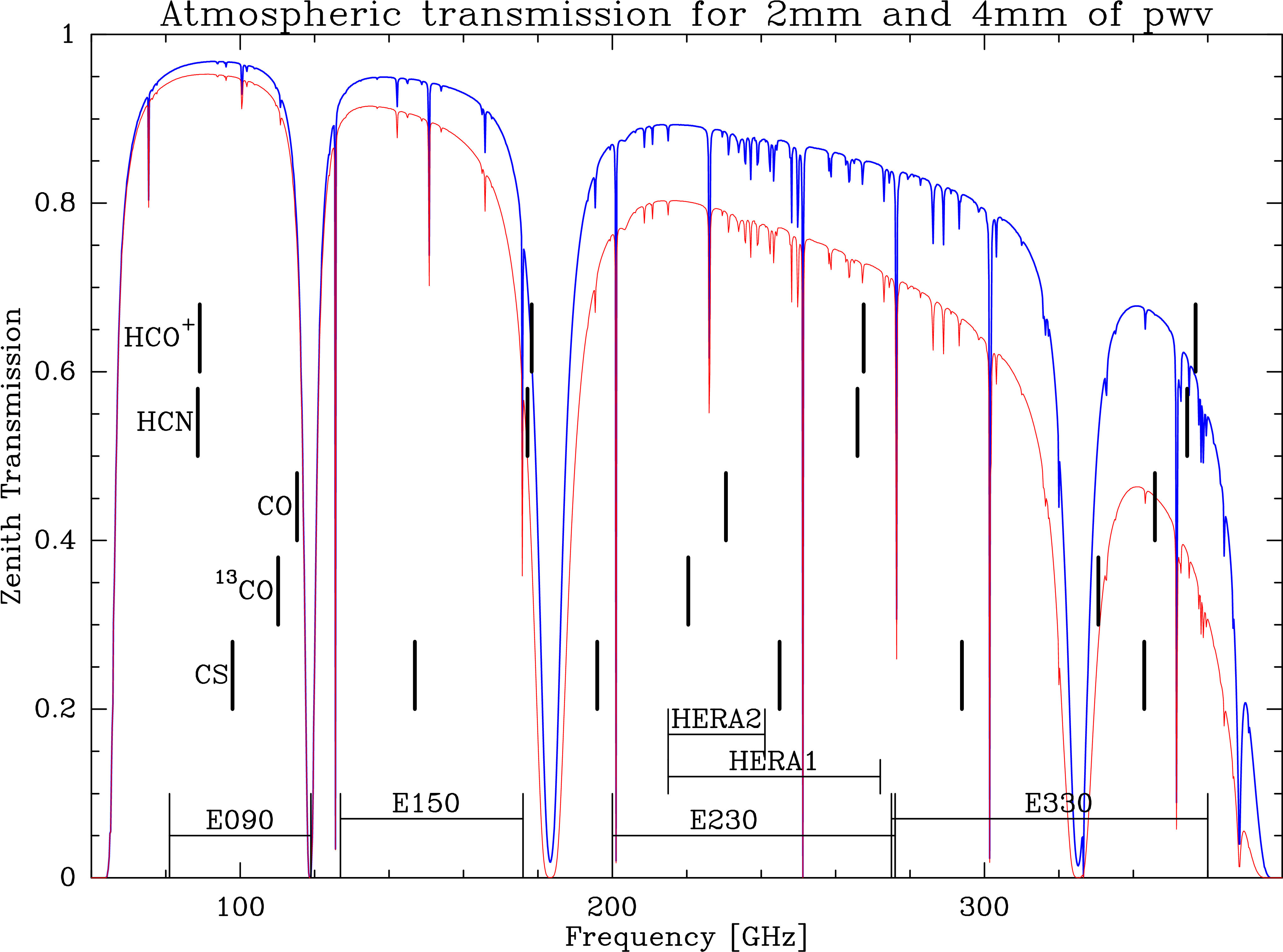
Figure 1: Atmospheric transmission between 60 and 400GHz for two precipitable water vapors, modeled with the ATM model. The EMIR bands are marked together with the frequencies of a few important molecular transitions.
EMIR bands
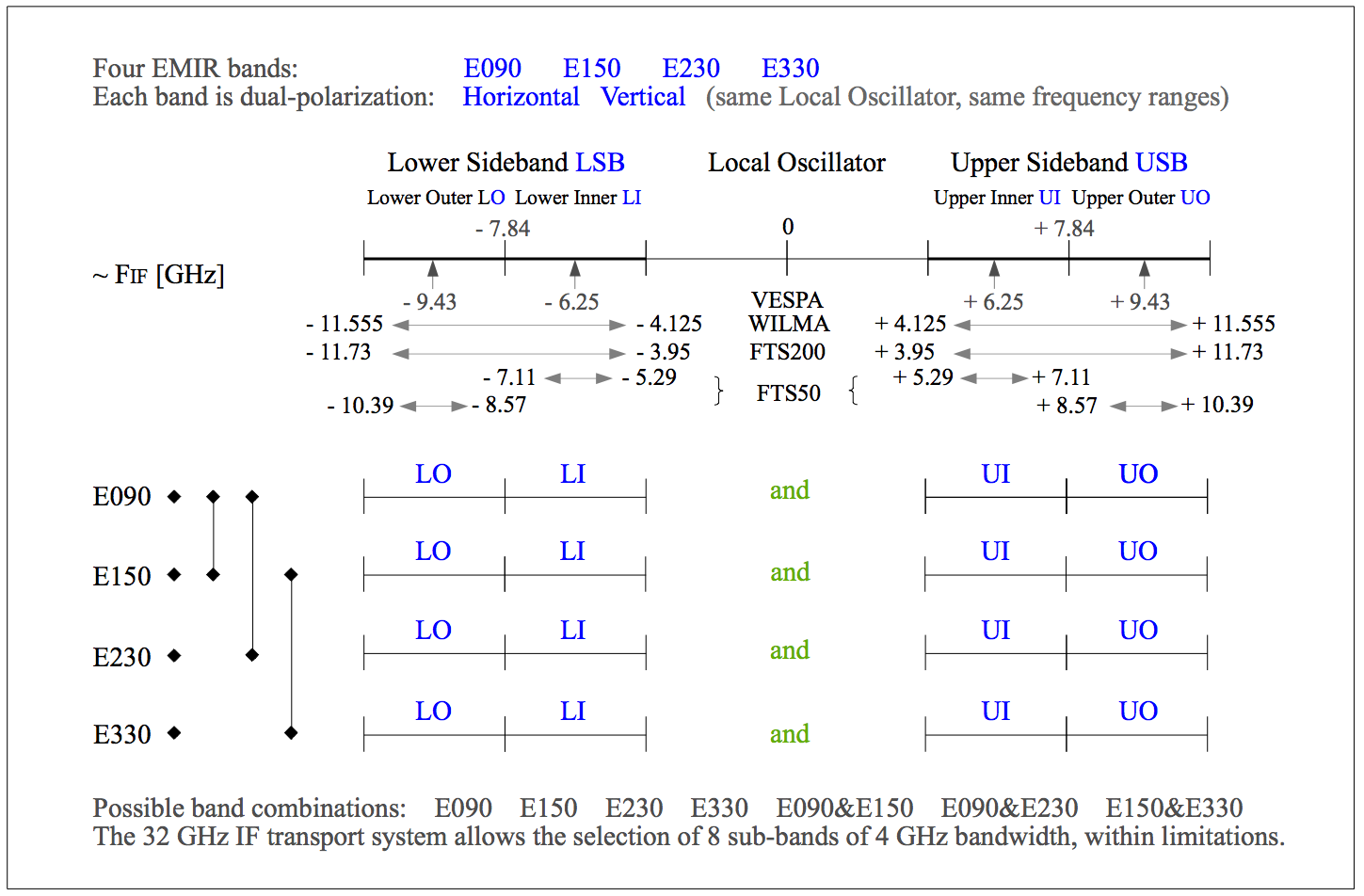
Figure 2: Overview of EMIR band combinations and frequencies which are available after the EMIR upgrade and commissioning in September/October-2013. Central frequencies of the (sub-)bands refer to VESPA, and the band edge frequencies are given for WILMA and the FTS backends in the two resolution presets. Frequency edges are taken from the list provided by G.Paubert on the backends page.
EMIR band combinations
EMIR has four different bands covering the four main atmospheric windows in the millimetre range: E090, E150, E230 and E330. Dual band observation is possible but only the E0/E1, E0/E2 and E1/E3 band combinations are allowed by the receiver optics. Each of the four bands (E0, E1, E2, and E3) have four IF outputs: 2 polarizations (H,V) and 2 sidebands (L,U), each of them is 8 GHz wide. The 8GHz wide IF outputs are split in two blocks, 4 GHz wide each, denoted by I and O (inner and outer) and sent to the spectrometers by the use of in total 8 coaxial cables. This means that a total of 32GHz of bandwidth are transferred to the spectrometers. In the future, we plan to upgrade the IF-system and backends to allow for 64GHz of total bandwidth, the maximum EMIR offers.
The FTS backends can be connected to all 8 cables, while the old backends VESPA and WILMA can only be connected to IF cables 1-4.
When designing the new switch box, we assumed that most will want to use both polarisations simultaneously. Aside from improving the signal-to-noise ratios, this observing mode allows for easy checks of the relative calibration.
Commissioned EMIR band combinations or setups:
One band only:
E0 LI+LO, UI+UO (dual-pol, 16GHz bandwidth)

E1 LI+LO, UI+UO (dual-pol, 16GHz bandwidth)

E2 LI+LO, UI+UO (dual-pol, 16GHz bandwidth)

E3 LI+LO, UI+UO (dual-pol, 16GHz bandwidth)

E2 LO+UO (special setup to use only IF bands 1-4, allowing to connect VESPA e.g. for polarimetry)
E0/E2:
E0: UI+UO, E2: UI+UO (dual-pol, 16GHz, e.g. 12CO, 13CO 1-0, 12CO 2-1)

E0: LI+LO, E2: LI+LO (dual-pol, 16GHz, e.g. HCN, HCO+ 1-0, 13CO 2-1)

E0H: LO+LI+UI+UO, E2V: LO+LI+UI+UO (single-pol, 32GHz, H<->V)

- Special setups (not tested after the upgrade in Sep-2013):
E0VUO (12CO 1-0), E2VUI, E2HUI (12CO 2-1), E2HLI (13CO & C18O 2-1) [only 4 IF-cables used]
E2HLI, E2HUI, E0VUI (or any other E0V band) (12CO & 13CO 2-1 + 3mm) [single-pol]
- E2UO, E2UI, E0UO, E0UI (using IF-cables 1-4, 12-Jan-2012)
E0LOH, E0LOV, E0UIH, E2LIV (HCN/HCO+ in dual-pol, 13CO 1-0 & 2-1 in single-pol; seems possible but has not been tested)
E1/E3:
E1: UI+UO, E3: UI+UO (dual-pol, 16GHz)

E1: LI+LO, E3: LI+LO (dual-pol, 16GHz)

E1H: LO+LI+UI+UO, E3V: LO+LI+UI+UO (single-pol, 32GHz)

- Obsolete setups after Sep-2013:
- E1V+E1H+E3VL+E3HL
- E1LI, E3LI, E3LO (dual-pol)
- E1UI, E3LI, E3VLO (dual-pol)
- E1UI, E3UI [after the switchbox upgrade in Oct-12]
- E1LI, E3UI [after the switchbox upgrade in Oct-12]
E0/E1:
E0: UI+UO, E1: UI+UO (dual-pol, 16GHz)

E0: LI+LO, E1: LI+LO (dual-pol, 16GHz)

E0H: LO+LI+UI+UO, E1V: LO+LI+UI+UO (single-pol, 32GHz, H<->V)

- Obsolete setups after Sep-2013:
- Together with E1, only the lower bands of E0 can be observed in dual-pol. Inner and outer bands can be observed simultaneously for E0. Important application: CS 2-1, 3-2.
- EOLI, E0LO, E1LI (dual-pol)
- E0LI, E0LO, E1UI (dual-pol)
- E0UI, E1UI [after the switchbox upgrade in Oct-12]
- E0UI, E1LI [after the switchbox upgrade in Oct-12]
- E0LOH, E0LIV, E0UIH, E1LIV ! special setup, as only one polarisation is used. Allows to observe three transitions of NH2D simultaneously.
Setups which are not possible:
3mm: UI+UO, 1mm: LI+UI (12CO, 13CO 1-0 & 2-1) ! Only a maximum of 4 inner cables can be selected.
- E0 LI,UI + E2 LI,UI ! Only a maximum of 4 inner bands can be selected. In general, when connecting to E2 LI+UI with both polarisations, none of the inputs of E0 are accessible.
- E0 LO UO + E2 LO LI
- 50kHz FTS: C18O, 13CO, 12CO 1-0 simultaneously. These lines lie 5.49GHz apart, while the outer edges of the FTS 50kHz units in the inner and outer band of EMIR lie 5.42GHz apart. The inner edges lie 1.78GHz apart. However, it is no problem to observe these lines simultaneously with 200kHz resolution.
- E0 alone with only two If cables attached, e.g. horizontal LI vertical LI, results in corrupted FTS raw data (imbfits files that mira can not read and result in a Segmentation fault). A Workaround is to attach 4 cables, e.g. horizontal UI+LI and vertical UI+LI.
More details on the selection rules and a sketch of the switch box, are given here: SwitchBoxDetails. See also the commissioning report below.
Focal plane geometry
The four bands will be combined in only two possible beams (left and the right beams when looking to the cryostat front face). The left and right beams are offset by about 90" on the sky. See the telescope status page for the present Nasmyth offsets (cf. EMIR Commissioning report below). Observations are carried out with either of the two beams. Simultaneous observations with both beams are at present not supported.
Selection of EMIR bands (Dichroics)
 Before reaching the Nasmyth mirrors, the four beams of the EMIR bands pass through warm optics that contains switchable mirrors and dichroic elements for redirection of the beams towards calibration loads and for combining beams. In its simplest mode, the warm optics unit selects one single EMIR band for observation. This mode avoids the use of the slightly lossy dichroic elements and therefore offers the best receiver noise temperatures.
Before reaching the Nasmyth mirrors, the four beams of the EMIR bands pass through warm optics that contains switchable mirrors and dichroic elements for redirection of the beams towards calibration loads and for combining beams. In its simplest mode, the warm optics unit selects one single EMIR band for observation. This mode avoids the use of the slightly lossy dichroic elements and therefore offers the best receiver noise temperatures.
Three dichroic mirrors are available for combining either the E090 and E150 beams, or the E090 and E230 beams, or the E150 and E330 beams (Table 1). The combination of bands is not polarization selective, i.e. the combined bands will stay dual polarization. The loss of these dichroics increases however the receiver temperatures by, in general, only 10 - 15 K. The losses of E2 (due to the use of the dichroic) are higher than 10% for frequencies above ~258GHz and below ~202GHz (cf. Table 2). The polarization angle of the dichroic was chosen to minimize the losses for 231GHz. The observer is therefore adviced to carefully evaluate whether an observation involving two different bands is more efficiently made in parallel or in series.
Simultaneous observations of e.g. HCO+ at 89.7 and 266.5GHz with E0 and E2, are possible after the replacement of the E0/E2 dichroic in September 2016.
The dichroics are needed for dual-band observations with EMIR. The following table shows the losses of the dichroics, based on a separate mixer and dichroic characterization done in the receiver lab by Anne-Laure Fontana in Feb 09.
Table 2: Performance of dichroics (February 2009, Report of Anne Laure):
E0/E2 |
E0/E1 |
E1/E3 |
|||||||||
E0 |
E0 |
E2 |
E2 |
E0 |
E0 |
E1 |
E1 |
E1 |
E1 |
E3 |
E3 |
GHz |
% |
GHz |
% |
GHz |
% |
GHz |
% |
GHz |
% |
GHz |
% |
84-108 |
2.5 |
202 |
10 |
84 |
4 |
129 |
5 |
129-138 |
2.5 |
261-357 |
<2.5 |
116 |
<2 |
213 |
5 |
92 |
3.2 |
138-156 |
1 |
147 |
4.5 |
369 |
7 |
|
|
225 |
3 |
100-110 |
5 |
168 |
2 |
156 |
3.5 |
|
|
|
|
231 |
2 |
110-115 |
~10 |
171 |
2 |
174 |
2.5 |
|
|
|
|
243 |
5 |
|
|
174 |
2 |
180 |
~5 |
|
|
|
|
255 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
258 |
10(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
267 |
50(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each percent of losses, increases the receiver temperature by about 4K.
(1) Note that these values have much improved after the replacement of the dichroic D13 in September 2016!
IF Distribution
An overview of the current disbribution of intermediate frequencies (IF) is given here.
Connection to backends
Eight output channels are sent via the IF cables to the backends at the IRAM 30m telescope:
- the Fast Fourier Transform Spectrometers (FTS) handle input from all 4 cables.
- The other backends take as input the (old) IF cables 1-4 only: Three backend processors have been build to feed the new 4 GHz wide IF channels to the existing backends:
The WILMA processor rearranges the four incoming 4 GHz wide IF channels into 16 channels of 1 GHz width which can be processed by 16 WILMA autocorrelator units. Since each unit provides 512 spectral channels of 2 MHz, sufficient backend power is available at low spectral resolution for full coverage of the 4x4GHz bottleneck.
The narrow backend processor prepares the 4 incoming IF channels for input into VESPA. Only the central part of the 4 GHz IF channels is accessible to these backends. Inside this central part (1 GHz for the filterbank and 640 MHz for VESPA), these backends can be configured as before. The VLBI terminal is also fed from this processor.
When planning to observe several interstellar lines simultaneously with EMIR, it is sometimes difficult to check whether this is possible with the FTS at 50kHz resolution and VESPA. GILDAS versions of July 2016 and younger, include a powerful tool, ASTRO\EMIR, to prepare the detailed frequency setups. This supersedes the following small GREG script, to help finding a local oscillator frequency to allow for simultaneous observations of several lines with both sidebands of one of the four EMIR receivers. The greg-script plots the frequency coverage of the FTS at 200 and 50kHz, and the 500MHz bandwidth of VESPA, together with a set of lines to be observed, using a given LO frequency:
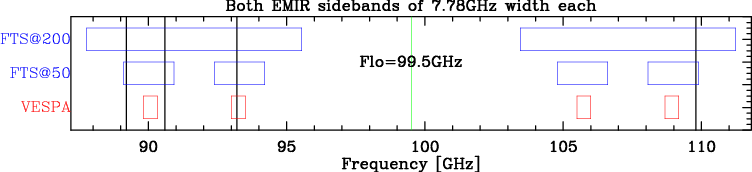
Figure 3: Frequency coverages of the various backends.
Temperature calibration
EMIR comes with a new calibration system. The external warm optics provides ambient temperature loads and mirrors reflecting the beams back into the 15 K stage of the cryostat. This system is expected to be very reliable and constant over time. Absolute calibration accuracy will be better than 10% with EMIR when all details are well settled.
All bands have tunerless sideband separation mixers, allowing simultaneous observations of both sidebands in separate IF bands. These mixers have been characterized in the laboratory for their image rejection and are expected to have the same performance on site (>13dB).
Correct frequency scales over upto 24 GHz of bandwidth
It is common practice at radio observatories to correct the frequency of an observation for the strongly time variable velocity of the Observatory with respect to the solar system barycenter. This guarantees that lines observed near the Doppler-tracked frequency, usually the band center, always have the correct barycentric velocity, independent of the time of observation. At the 30m, the local oscillator and its synthesizers are constantly adjusted during observations to track the changing Doppler factor for one spectral line with its rest frequency. This causes a slight shift of lines observed simultaneously at a diff erent frequency. This shift is proportional to the frequency diff erence and the Doppler factor. CLASS corrects for this shift by adapting the spectral resolution.
As the report below describes, these shifts correspond to time variable changes of the frequency resolution. Co-adding or averaging spectra taken at different times, may then lead to a broadening of the effective frequency resolution.
Accurate line center frequencies: Report of 03-Aug-2011 by Buchbender, Kramer et al.. Two bugs in mira and class caused frequency shifts and have been corrected for. The new versions of mira and class were installed at the 30m on 16-Aug-2011.
PaKo user interface
The new default PaKo version supports the upgraded E2 and E3 mixers and the enhanced IF switch box. See the current PaKo manual.
Please contact your astronomer-of-duty to help you prepare scripts or in case of any questions.
EMIR Observations Time Estimator
Telescope efficiencies
Alignment
The current alignment between polarisations and between EMIR bands is given here.
Observatory status
Reports and publications
Suppression of E230 ghost lines after installation of an LO filter, 25-Apr-2017, Marka, Navarro, John.
EMIR Upgrade of Dichroic D13 in 2016 – Tests in NCS at PV, H. Ungerechts et al.. 1-Feb-2017
Report on E230 ghost lines from unwanted 7th harmonic of the LO, 20-Jan-2017, Marka and Navarro.
Commissioning Report on XPOL E090 with OMT, 1-Apr-2016 by A. Sievers.
Report on suppression of E090 ghost lines after installation of an LO filter, 31-March-2016, Navarro and Marka.
Report on E150 ghost lines from unwanted 5th harmonic of the LO, 16-March-2016, Marka and Navarro.
Commissioning of the upgraded E090 and E150 bands (15-Dec-2015, C.Marka and C.Kramer)
Commissioning Report on XPOL using the New Optics, 19-Oct-2015 by Sievers et al.. For more information on XPOL, see here.
Commissioning Report on the New Optics, 29-May-2015 by Ungerechts et al.
Report on E150 image band rejections, 30-March-2015 by Marka et al.
Report on suppression of E150 ghost lines after installation of an LO filter, 26-March-2015 by Sievers et al.
Report on EMIR ghost lines (unwanted harmonics of the local oscillators, 21-August-2014 by Kramer, Navarrini, Navarro, John, Cernicharo
Report on E1 optics in the 122 - 186 GHz range: performance at the band edges, July 2014 by Anne Laure Fontana (IRAM/Grenoble)
Report on Lab measurements of EMIR receivers: receiver temperatures and image band rejections, June 2014 by Doris Maier (IRAM/Grenoble)
The EMIR Multi-band mm-Wave Receiver for the IRAM 30m Telescope, Carter, Lazareff et al. 2012 (A&A, 538, 89)
The current beam pattern of the 30m telescope is described in a new report, based on EMIR observations covering the entire frequency range between 86 and 345GHz. The main beam efficiencies have considerably improved relative to the values compiled in Greve et al. (1998). See here or here.
- Commissioning Reports:
Bands 1-3: EmirCommissioningReportVers1.1.pdf (4/2009)
Band 4: emir-e3-com-report-05apr2010.pdf (4/2010)
Polarimetry (Bands 1&3) wiesemeyer-thum-xpol-report-10aug2010.pdf (8/2010)
Upgrade to 32GHz IF system kramer-aug2011-32ghz-newsletter.pdf (7/2011)
- Upgrade of E2 and E3 mixers (Nov 2011)
emir-nov11-com-report-v1.0.pdf Report on spectral line commissioning observations by Kramer et al.
e2-09apr2012.pdf Report on E230 issues encountered till 23-February-2012.
Historic news
E090: Spectral sidelobes have not been detected anymore in E090H, after swapping the mixer bias boxes of E090 and E330 on 22-January. E330 has also been checked and shows no such problems. These "spectral sidelobes" had been an issue after the upgrade of E090 in November last year. <27-Jan-2016>
E090: The following issue has been resolved by installing a filter in the local oscillator path on 22-Mar-2016 (see a short report here). Before that date, the unwanted 3rd harmonic of the Gunn oscillator of E090 local oscillator had not been sufficiently suppressed. It had leaked through to the mixers and lead to detection of strong lines stemming from outside the observed band.
The new receiver cabin optics has been installed and optically aligned: To prepare for NIKA-2 and future heterodyne array cameras new, larger mirrors M3 and M4 have been installed, together with new mounts. EMIR mirrors M5, M6, and M7 also had to be adapted, and HERA was moved a few cm to its new position. After a successful optical alignment, astronomical commissioning using all bands of EMIR went well without major issues. Commissioning of HERA also went well. (cf. A report is available online). <29-May-2015> The commissioning report on polarimetry with EMIR XPOL is available here. <19-Oct-2015>
Image band rejections of E150 have degraded since installation of the new dual-sideband (2SB) mixers in September 2013, in particular for the Vertical Polarisation. The average rejection is now about -7dB (factor 5) instead of -13dB (factor 20). This finding is currently being discussed with the receiver groups in Granada and Grenoble. (cf. report of 30-March-2015). The gain ratio depends to some degree on the LO and mixer settings as this report and also the lab report shows. As the antenna temperature is proportional to (1+GainRatio), observers interested in a high calibration accuracy may want to measure the gain ratio as function of frequency for their particular observational setup using both sidebands simultaneously, e.g. on a line calibrator source.
To suppress any "ghost" lines in E150, a filter of the local oscillator was installed on 2-Dec-2014. The outer edges of E1 can still be reached and E1 has been used since then without problems. The filter works very well (cf. report of 25-March-2015).
E330 YIG LO has been installed (LO-range 283-365GHz) (see below). <Oct-2014>
- Observers who intend to observe beyond the frequency ranges offered on the EMIR homepage should contact the Granada receiver group at least a week before the start of observations, even if these frequencies had previously been observed. This is to allow for time to check again if needed and inform the operators.
A report on gain ratios and receiver temperatures from lab measurements of the installed EMIR mixers for all four bands has been prepared by D.Maier (IRAM/Grenoble). See also the comment 1.2. in Table 1 on the recommended LSB frequency range of E090.
E150 frequency range: Information on the E150 frequency range has been updated (cf. Table 1). See also a report by A.L.Fontana (IRAM/Grenoble) on the system performance of E150 at its band edges.
EMIR Ghost Lines: The EMIR local oscillators (LOs) do create harmonics of its Gunn oscillators, which are mixed in the sideband separating mixers, and then down converted into the IF (intermediate frequency) band. The LOs do, however, also create unwanted harmonics which may not be sufficiently suppressed, leak through, and pump the mixers. This may lead to detections of ghost lines stemming from much higher frequencies, far outside the nominal frequency range, polluting the observed spectra. Such lines have recently been identified in frequency surveys of IRC+10216: in one example, a ghost line showed-up at 129GHz in the E150 band, which does however stem from a line at 196GHz. With the large bandwidths provided by EMIR, and with deep frequency surveys on bright Galactic star forming regions like Orion showing a large dynamic range of line temperatures, addressing these ghost lines becomes important. A report has been prepared to inform the observers of the current status of this issue, describe the origin of the harmonics, give observational examples showing also how to detect ghosts, and describe counter measures which are currently being prepared by the IRAM frontend groups. <21-August-2014 CK>
The script to check the possibility to observe several lines with one of the EMIR receivers and the present set of backends, has been updated now providing more information on the frequency distance to the edges of the bands and on possible sky frequencies for pako. See below "Connection to Backends".
The current beam pattern of the 30m telescope is described in a new report, based on EMIR observations covering the entire frequency range between 86 and 345GHz. The main beam efficiencies have considerably improved relative to the values compiled in Greve et al. (1998). See here or here.
- The local oscillator for EMIR band 4, E330, had to be sent to Grenoble for repair. We re-installed the Gunn LO with its upper frequency limit of 358 GHz. (12-February-2014)
- News on the upgrade of E150 and E330 in Sep-2013:
- Installation of the new 2SB mixers for E150 and of the new YIG LO for E330, went well. New versions of pako and of the software controlling the IF switchbox have been tested and implemented. A commissioning report is in preparation.
E1 frequency survey between 125 and 186GHz went well. Same for tests of the basic setups of the IF switchbox. All successfully tested setups are marked with a
 in the listing of setups below.
in the listing of setups below. - E3 has been tested at local oscillator frequencies between 300 and 360 GHz.
- Installation of the new 2SB mixers for E150 and of the new YIG LO for E330, went well. New versions of pako and of the software controlling the IF switchbox have been tested and implemented. A commissioning report is in preparation.
Antenna temperatures of E1 upper sideband (USB) observations at sky frequencies between 144 and 147 GHz have been found to be a factor ~2 lower than lower sideband (LSB) spectra due to a wrong tuning table leading to a poor image band rejection. The tuning table was wrong since the installation of EMIR in 4/2009, but has been corrected now. We have found no indications for such problems outside the above frequency range. <9-Jan-2013 CK>
We have implemented a small upgrade of the IF switchbox which now allows simultaneous observations of E3 in USB together with E1, and of E0 USB together with E1. The former setup will be helpful for high frequency E3 observations together with pointings using E1. All previously possible IF setups stay available after this upgrade. See switch box details below. <28-Oct-2012 CK>
The local oscillator for E330 has been refurbished such that EMIR can now reach sky frequencies up to 358 GHz, giving access to the 4-3 transitions of HCN and HCO+ under excellent weather conditions. <30-Jul-2012 CK>
A dedicated paper on the working of EMIR and first results has been published by Carter, Lazareff et al. 2012 (A&A, 538, 89).
- Observers have been informed on 26-Apr-2012 on problems for some frequencies with E230 between 15-Nov-2011 and 23-Feb-2011 when this band showed excess noise, spurious signals, and calibration problems. Improving on the tuning parameters solved this.
- The E0/E1 alignment is better than 1", after repositioning the EMIR caroussel no. 2 on 29-Nov-2011, and later replacing its position sensor.
- The main EMIR band setups possible after the upgrade of E2 and E3, and of the IF switch-box, have been successfully commissioned in November 2011. Possible EMIR band combinations are detailed below.
This page is maintained by C.Kramer. Any comments are welcome.
