Observing session
Observations are carried from a dedicated pool account (ask the AoD for the login information). Each project has a folder within the home directory of the pool account with instructions on how to proceed. Read carefully the README file before to start. For example, the file ~/193-13/README_193-13.txt shows you how to observe the project 193-13.
Contents
Choose a project
First log into the Pool data base (ask the AoD for the login information) and click on the GISMO/NIKA tab.
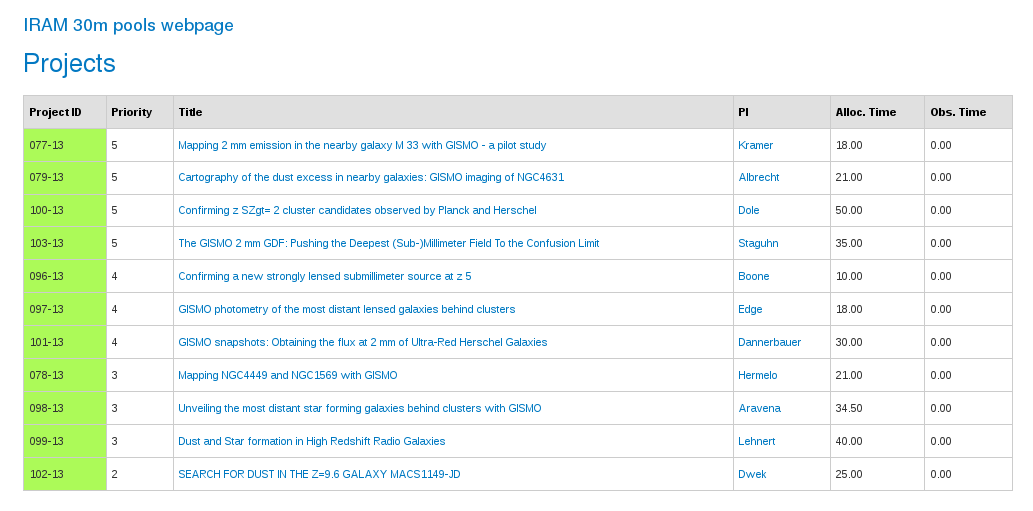
Projects have different priorities from 6 (highest priority) to 1 (lowest priority). Green color indicates that the project is scheduled, orange that the project is on hold, and red that the project is finished. Only green projects should be observed. To check the visibility of these projects go to the visibility tab:
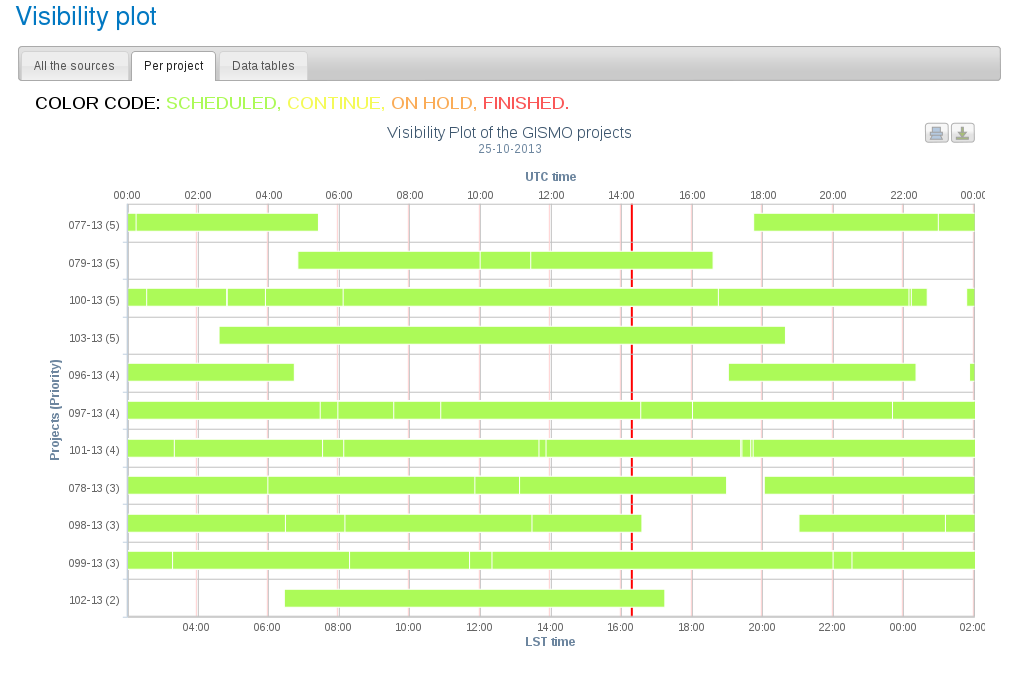
The red vertical line corresponds to the current time (UT). In this example there are four priority 5 projects. Project 077-13 is not visible at the current time. Project 079-13 is close to the low elevation limit so it is a bad option. Since project 103-13 sets first, you should first observe this project. After 2-3 hours change to project 100-13. In case that none of the priority 5 projects have weather requirements (see the README files) compatible with the current conditions, go for priority 4 projects and so on.
Starting PaKo
To run the observations at 30m telescope it is necessary to start a PaKo session. First log into the mrt-lx1 machine:
$ ssh -X pool_account@mrt-lx1.iram.es (ask the AoD for the name of the pool account and the password)
Then start PaKo:
$ gopako $ pakodisplay $ pakoGISMO or pakoNIKA
With these commands, PaKo will be running in the '~/PaKo/' folder.
Starting XEphem
Log into the mrt-lx3 machine:
$ ssh -X pool_account@mrt-lx3.iram.es
Type:
$ useNCS $ azElToXephem.py & $ .xephem/xephem.exe &
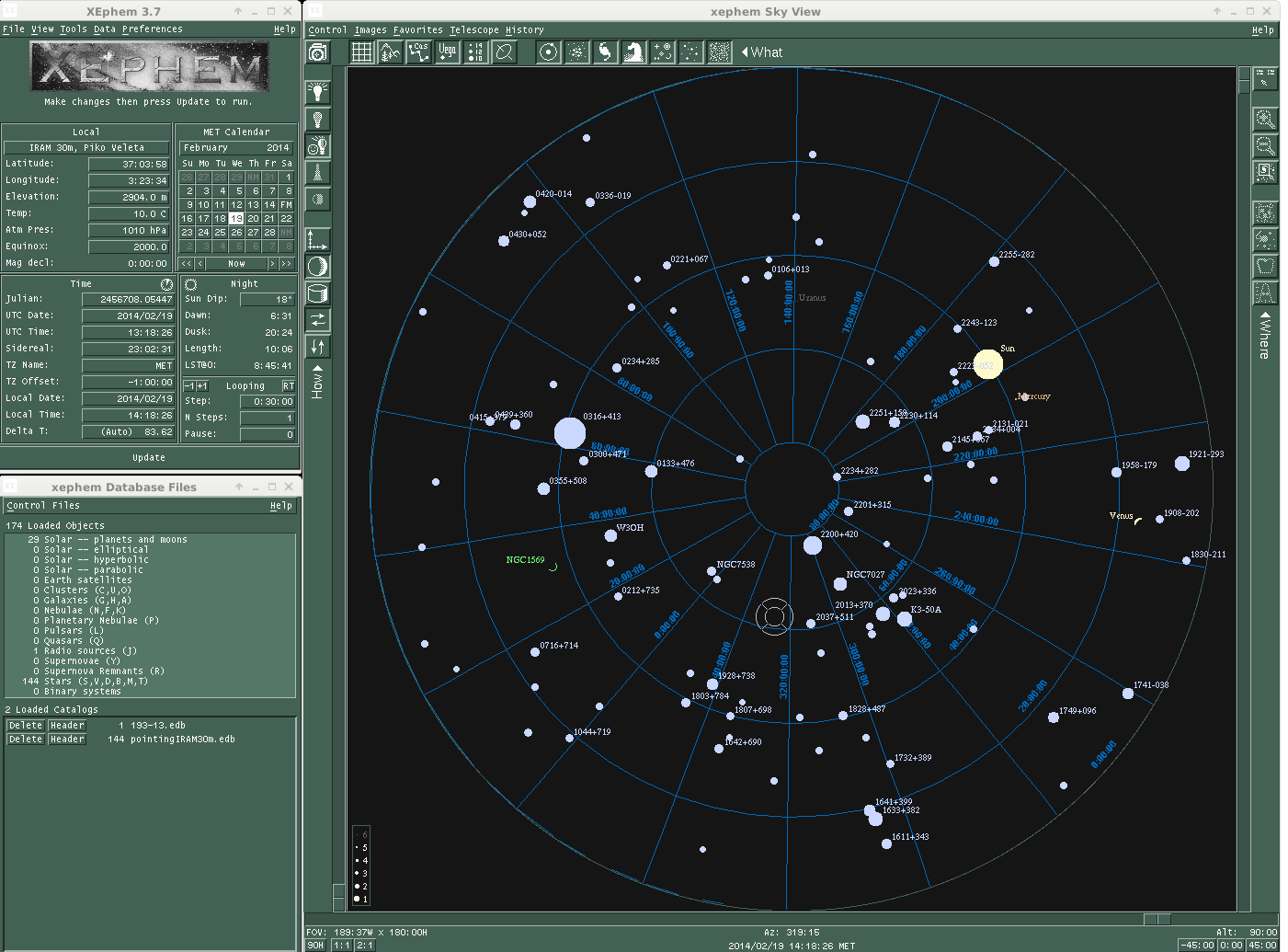
Click on the tab "View" and open the "Sky View". The "cross hair" shows the coordinates the telescope is pointing at. The filled blue circles are the pointing sources. The size of the circle is proportional to the flux of the target. Click on the tab "Data" and go to "Files". In the new window go again to "Files" and load the catalog of the project that you are observing.
Project setup
The standard method to set the project is:
PAKO> set project XXX-YY
However, for pooled observations this is often done using a setup script (see for example setup_193-13.pako). For example, before to start to observe the project 193-13 you should type:
PAKO> @ ~/193-13/setup_193-13.pako
It is IMPORTANT to set the project accordingly before each observation in order to identify the scans observed for each project, keep control on the time used to observe each project, and write the data files in the right directory. When you will be doing tests, or if you have to stop by wind, or whatever, just type "set project test". That way, no project will loose time due to technical problems, or bad weather.
Catalog of sources
Before to start to observe a certain project it is necessary to load its catalog of sources. Usually, this is automatically done within the setup script. If for some reason you need to load the catalog manually, type:
PAKO> SOURCE CATALOG 193-13.sou
This command will load the following list of sources:
NGC1569 EQ 2000 04:30:50.5 +64:50:55 LSR 0.0 NGC4449 EQ 2000 12:28:09.4 +44:05:32 LSR 0.0
To select any of these sources just type:
PAKO> source NGC4449
Pointing
Check in the PaKo display for the current pointing values (AZcurrent and and ELcurrent) and write them down. Choose a nearby quasar as pointing and focus source (using e.g. XEphem):
PAKO> source 0133+476 /cat *
Launch the cont_pointing script:
PAKO> @ cont_pointing
This script will launch a 1'x1' Lissajous map that takes 2 minutes. Once the pointing is finisihed, enter the pointings corrections:
For GISMO, check in the Nexus logsheet for the corrections in azimuth and elevation (columns pnt.dAZ and pnt.dEL), and calculate the new pointing values as:
AZnew = AZcurrent + pnt.dAZ ELnew = ELcurrent + pnt.dEL
For NIKA see the data reduction wiki and ask the AoD.
If the new pointing corrections are within 10" of the previous values, the array with its large field-of-view will still be well centered. To update the pointing constants used by PaKo, type:
PAKO> set pointing AZnew ELnew
Focus
The focus needs to be monitored every two hours or so, and it needs to be corrected online! To check the quality of the focus, type:
PAKO> @ cont_focus Fcurrent
where Fcurrent is the current value of the focus.
This script will send 5 1'x1' Lissajous maps performed with 5 different values of the focus. Each map will take 1 minute. Once the 5 scans are finished, follow these instructions to calculate the optimal value of the focus:
For GISMO open another terminal and use the python script ~/Focus/Focus.py :
$ cd Focus/ $ python Focus.py
The python script will ask for the 1st scan of the focus sequence and the total number of scans (i.e., 5). Check if the two estimations shown (see image below) in the plot are consistent.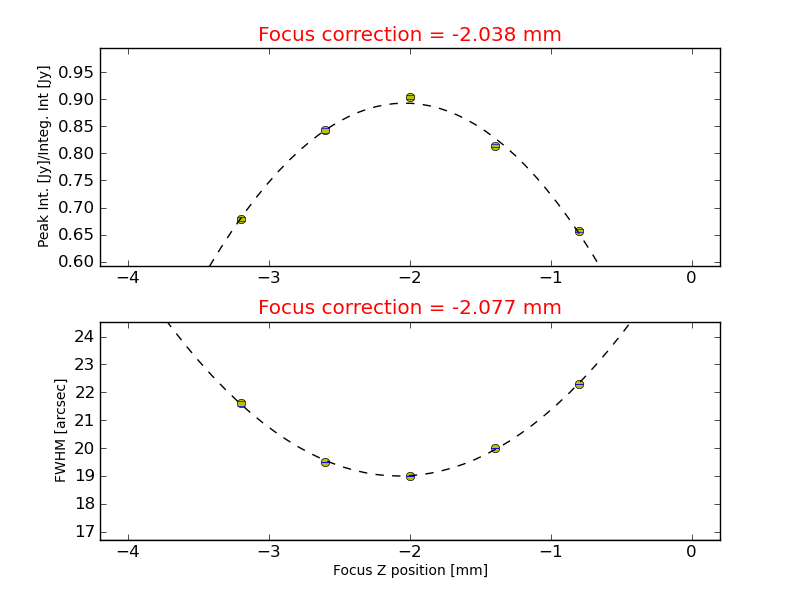
For NIKA see the data reduction wiki and ask the AoD.
Finally, enter the new value:
PAKO> set focus Fnew
Now the telescope is pointed and focussed, and ready to start to observe.
Science targets
Observations of science targets are performed via on-the-fly and/or Lissajous maps. For example, for a 16'x12' on-the-fly map rotated 25 degrees (measured anticlockwise) type:
PAKO> @ cont_onthefly 16 12 25
For a 3'x3' Lissajous type:
PAKO> @ cont_lissajous 3
A sequence of several scans can be commanded using scripts. For example, the script observe_NGC4449.pako combines several 10'x10' on-the-fly maps covering the whole galaxy environment and 4'x4' Lissajous maps to optimize the signal of the central regions. To launch this script just type:
PAKO> @~/193-13/observe_NGC4449
Beam map
The beam map consists in a 5'x5' map with ~3" steps between rows and a duration ~18 min for GISMO, and 6.7'x3.7' map with 4" steps between rows and a duration ~12 min for NIKA. Beam maps are designed to ensure the source is moved over all the detectors of the array, in order to characterize and calibrate them (field of view geometry, flat field, stability...). The aim is to calculate the actual pixel offsets in the focal plane (see figure below). To obtain a beam map go to a primary calibrator and launch the cont_beammap.pako script:
PAKO> @ cont_beammap
Skydips
To run a skydip with the IRAM continuum cameras, launch the cont_skydip script:
PAKO> @ cont_skydip
Please note that when using GISMO, before running a skydip, the observer has to de-activate the automatic relocking of the detectors:
NEXUS -> Configuration -> Advanced -> De-activate automatic relock of detectors
And once the skydip is finished, the observer needs to switch-on by-hand the automatic relocking of the detectors:
NEXUS -> Configuration -> Advanced -> Activate automatic relock of detectors
Obsolete scripts
A set of fully tested scripts from previous runs are available within the ~/PaKo/obs/ folder. The following list shows how to launch some of the most popular obsolete scripts:
GISMO
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_pointing.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_2mx2m.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_3mx3m.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_4mx4m_2min.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_4mx4m.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_5mx5mfast.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_5mx5m.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_GDF.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_tiny1min.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_tiny2min.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_tiny4min.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_tiny5min.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_tiny10min.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_otf_6mx6m.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_otf_8mx8m.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_otf_10mx10m.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_otf_30mx30m.pako
PAKO> @ obs/gismo_otf_beammap.pako
NIKA
PAKO> @ obs/cross.pako
PAKO> @ obs/diydown.pako
PAKO> @ obs/diyup.pako
PAKO> @ obs/faintliss1.pako
PAKO> @ obs/faintliss1t.pako
PAKO> @ obs/faintliss2.pako
PAKO> @ obs/faintlissfast.pako
PAKO> @ obs/faintliss.pako
PAKO> @ obs/faintlisst.pako
PAKO> @ obs/focusliss.pako
PAKO> @ obs/focusp2.pako
PAKO> @ obs/focusp.pako
PAKO> @ obs/ngc891liss.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otf10x10.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otf10x2.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otf15x10.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otf3x3_el.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otf3x3.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otf4x2.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otf4x4.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otf5x5_half.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otf5x5.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otf5x5_pol.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otf5x5slow.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otfgeom.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otfgeom_pol.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otf.pako
PAKO> @ obs/otfsz.pako
PAKO> @ obs/pointliss.pako
PAKO> @ obs/pointliss_pol.pako
PAKO> @ obs/skydip.pako
PAKO> @ obs/skydip_test.pako
PAKO> @ obs/skydip_updown.pako
PAKO> @ obs/skydip_up.pako
Author: Israel Hermelo (IRAM 30m Continuum Pool Manager)
email: hermelo@iram.es
Created: 2013.Oct.25
Last update: 2014.Mar.02
