|
Size: 11578
Comment:
|
Size: 7242
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| #acl hermelo,CarstenKramer,NicolasBillot,SamuelLeclerc:read,write,delete,revert,admin Default | #acl PabloGarcia,CarstenKramer,SamuelLeclerc:read,write,delete,revert,admin Default |
| Line 3: | Line 3: |
| = Observing session = Observations are carried from a dedicated pool account (ask the AoD for the login information). Each project has a folder within the home directory of the pool account with instructions on how to proceed. Read carefully the README file before to start. For example, the file [[attachment:README_199-14.txt | ~/199-14/README_199-14.txt ]] explains you how to observe the project 199-14. |
= Observing with NIKA2 = |
| Line 13: | Line 7: |
| '''Go to the [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Continuum/GISMO/Main|GISMO]] |[[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/NIKA/Main|NIKA]] page.''' | '''Go to the [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Continuum/NIKA2/Main| NIKA2]] main page.''' |
| Line 17: | Line 11: |
| == For astronomers == | == Starting PaKo == |
| Line 19: | Line 13: |
| === Choose a project === | To start the !PaKo session for rgular obsevations, log into the pool account "nikas-17" (ask the AoD/operator for the login information), open a terminal and type: |
| Line 21: | Line 16: |
| First log into the [[https://pools.iram.es | Pool data base]] (ask the AoD for the login information) and click on the GISMO/NIKA tab. | {{{ $ ssh -X nikas-17-lx1 $ goNIKA $ PAKO> @ini $ PAKO> set project XXX $ PAKO> set doSubmit YES }}} |
| Line 23: | Line 24: |
| {{attachment:PoolDatabase.png | Pool data base | width=1000 }} | Now you are ready to start observations. |
| Line 25: | Line 26: |
| Projects have different priorities from 6 (highest priority) to 1 (lowest priority). Green color indicates that the project is '''scheduled''', orange that the project is '''on hold''', and red that the project is '''finished'''. Only green projects should be observed. To check the visibility of these projects go to the visibility tab: |
== Observations queue == |
| Line 30: | Line 28: |
| {{attachment:Visibility.png | Visibility plot | width=1000}} | To check what is currently in the observation's queue, open a terminal and type: |
| Line 32: | Line 30: |
| The red vertical line corresponds to the current time (UT). In this example there are four priority 5 projects. Project 077-13 is not visible at the current time. Project 079-13 is close to the low elevation limit so it is a bad option. Since project 103-13 sets first, you should first observe this project. After 2-3 hours change to project 100-13. In case that none of the priority 5 projects have weather requirements (see the README files) compatible with the current conditions, go for priority 4 projects and so on. |
{{{ $ ssh -X mrt-lx1 $ observationQueue }}} This will open a file browser with a list of all the observation's files commanded, which are waiting to be executed by the telescope's system. To remove any observation's file from the queue, right-click on the corresponding xml file and select "delete". The display will be automatically refreshed. ## Check the [[https://mrt-lx1.iram.es/mainWiki/NcsUG | NCS user guide wiki]] for more obs* commands. |
| Line 42: | Line 42: |
| === Starting PaKo === | == Starting the NIKA2 pipeline == |
| Line 44: | Line 44: |
| To run the observations at 30m telescope it is necessary to start a !PaKo session. First log into the mrt-lx1 machine: |
To have the IDL pipeline continuously processing observations as they are produced, open a terminal and type: |
| Line 48: | Line 47: |
| $ ssh -X pool_account@mrt-lx1.iram.es (ask the AoD for the name of the pool account and the password) | $ ssh -X observer@nika2-a (ask the AoD for the password) $ IDL IDL> nk_rta, scanID (e.g. '20151019s132') |
| Line 51: | Line 52: |
| Then start PaKo: | where scanID is the corresponding identifier of the observation (as shown in the example) in the format YYYYMMDDsXXX, where YYYY is the year, MM the month, DD the day, and XXX the scan number. == Starting XEphem == XEphem is the software currently used at the IRAM 30m telescope to keep track of the position of astronomical sources on the sky. To start XEphem, open a terminal and type: |
| Line 54: | Line 62: |
| $ gopako $ pakodisplay $ pakoGISMO2014 or pakoNIKA }}} With these commands, !PaKo will be running in the '~/PaKo/' folder. === Starting XEphem === Log into the mrt-lx3 machine: {{{ $ ssh -X pool_account@mrt-lx3.iram.es }}} Type: {{{ $ useNCS $ azElToXephem.py & |
$ ssh -X mrt-astro1 xephem or $ ssh -X mrt-lx3 |
| Line 78: | Line 68: |
| Click on the tab "View" and open the "Sky View". The "cross hair" shows the coordinates the telescope is pointing at. The filled blue circles are the pointing sources. The size of the circle is proportional to the flux of the target. Click on the tab "Data" and go to "Files". In the new window go again to "Files" and load the catalog of the project that you are observing. | Then, click on the tab "View" and open the "Sky View". The "cross hair" shows the coordinates the telescope is pointing at. The filled blue circles are the pointing sources. The size of the circles is proportional to the flux of the target. To load the sources catalog of your project, click on the tab "Data" and go to "Files". In the new window go again to "Files" and select the catalog of the project that you are observing. |
| Line 80: | Line 73: |
| {{ attachment:XEphem.png | XEphem example | width=1000 }} | {{ attachment:XEphem.png | XEphem example | width=850 }} |
| Line 82: | Line 75: |
| == Pointing == | |
| Line 83: | Line 77: |
| === Project setup === The standard method to set the project is: |
In order to correct the pointing of the telescope in a given part of the sky choose a nearby pointing source (using e.g. XEphem) and type: |
| Line 88: | Line 80: |
| PAKO> set project XXX-YY | PAKO> source 0133+476 /cat * (or "iram-J2000.sou" for the given catalog) |
| Line 91: | Line 83: |
| However, for pooled observations this is often done using a setup script (see for example [[attachment:setup_199-14.txt | setup_199-14.pako ]]). For example, before to start to observe the project 199-14 you should type: | Now launch the '''nkpoint''' script: |
| Line 94: | Line 86: |
| PAKO> @ ~/199-14/setup_199-14.pako | PAKO> @ nkpoint mode |
| Line 97: | Line 89: |
| It is IMPORTANT to set the project accordingly before each observation in order to identify the scans observed for each project, keep control on the time used to observe each project, and write the data files in the right directory. When you will be doing tests, or if you have to stop by wind, or whatever, just type "set project test". That way, no project will loose time due to technical problems, or bad weather. === Job queue of observations === Log into the mrt-lx1 computer using the pool account: |
where the keyword "mode" can adopt the values '''b''' for bright sources and '''f''' for faint sources (the '''l''' option for very faint sources that require the Lissajous pattern is no longer used). The pointing scans are currently reduced by the IDL pipeline. To obtain the pointing corrections, process the corresponding scan with the pipeline: "IDL> nk_rta, scanID". Once the pointing scan is processed, enter the new pointing corrections in azimuth (PnewX) and in elevation (PnewY) shown on the IDL prompt of the NIKA2 pipeline: |
| Line 105: | Line 95: |
| $ ssh -X pool_account@mrt-lx1.iram.es | PAKO> set pointing PnewX PnewY |
| Line 109: | Line 99: |
| Type | == Focus == The focus needs to be monitored and it needs to be corrected online. This should be done every three hours or so in the Z direction. To check the quality of the focus run: |
| Line 112: | Line 104: |
| $ observationQueue | PAKO> @ focusOTF-Z fz |
| Line 115: | Line 107: |
| This will open a file browser with a list of all jobs. The display is automatically refreshed. Right-click to delete a job. ## Check the [[https://mrt-lx1.iram.es/mainWiki/NcsUG | NCS user guide wiki]] for more obs* commands. |
Currently, this script will carry out 5 foci measurements in Z direction within a 1.6 mm range, centered at the fz value. In order to obtain the focus corrections, the corresponding scan number have to be processed by the IDL pipeline: {{{ IDL> nk_rta, scanID1 (for measurement 1) IDL> nk_rta, scanID2 (for measurement 2) IDL> nk_rta, scanID3 (for measurement 3) IDL> nk_rta, scanID4 (for measurement 4) IDL> nk_rta, scanID5 (for measurement 5) }}} Then, all measured foci need to be procesed together by the "nk_focus_otf" routine of the IDL pipeline to perform the best focus fit in terms of the mesured Flux, beam FWHM, and beam ellipticity of the KID's. This can be achieved by runnning the following instruction in the IDL prompt: {{{ IDL> nk_focus_otf,'YYYYMMDDs'+strtrim(SCANNUMBER+indgen(5),2) }}} where the ScanID is in the format YYYYMMDDsSCANNUMBER (e.g. '20151019s132'). Once the "nk_focus_otf" routine has finished, check the focus correction values displayed in the IDL prompt under "Fluxes" for the three arrays (A1, A2, & A3) and calculate the average value that will be used to correct the focus. Enter the new focus value (Fnew) as follows: {{{ PAKO> set focus Fnew }}} == Beam map == Beam maps are designed to ensure the source is moved over all the detectors of the array, in order to characterize and calibrate them (field of view geometry, flat field, stability, etc). The aim is to calculate the actual pixel offsets in the focal plane (see figure below). To obtain a beam map go to a primary calibrator and launch the '''beammap1scan99sub.pako''' script in the normal !PaKo session: {{{ PAKO> @ beammap1scan99sub (to produce 99 sub-scans, standard PaKo version) OPTION = a (ENTER OPTION: a = Az. scan, e = El. scan, l = lower than 60° in El., h = between 60° and 70° in El.) W-OTFMAP /TOTF, value 12.0 implies /speed 65.0 outside standard range 0.0 to 60.0 W-OTFMAP, WARNING--CONDITION: Elevation must be less than 69.03 [deg] OTFMAP 780''x 470.4'' (step 4.8) > Number of subscans: 99 > Scanning speed: 65 arcsec/sec > Time per subscan: 12 sec > Execution time: 23.1 min }}} {{attachment:beammap1scan99sub.png | Beammap 99 sub-scans | width=500 }} |
| Line 121: | Line 150: |
| == Skydips == | |
| Line 122: | Line 152: |
| === Catalog of sources === Before to start to observe a certain project it is necessary to load its catalog of sources. Usually, this is automatically done within the setup script. If for some reason you need to load the catalog manually, type: |
To run a skydip with NIKA2 type in !PaKo: |
| Line 127: | Line 155: |
| PAKO> SOURCE CATALOG 199-14.sou | PAKO> @ skydip |
| Line 130: | Line 158: |
| This command will load the catalog [[attachment:199-14.txt | 199-14.sou ]] with the position of NGC4449: To select this source, just type: |
The script will perform 11 measurements (30 [s] tracks) at different airmasses wrt. the position Az = 180°, El = 55° in the HORIZON coordinate system. The skydip takes ~6.4 minutes to be finished. == Science targets == Observations of science targets are performed via on-the-fly (OTF). For example, for a 10'x15' OTF map, with a position angle of 25 degrees, a tilt angle of 0 degrees (both measured '''anticlockwise'''), in equatorial coordinates (radec, for the HORIZON coordinate system set '''azel'''), just type: |
| Line 134: | Line 167: |
| PAKO> source NGC4449 | PAKO> @nkotf 10 15 25 0 20 40 radec |
| Line 137: | Line 170: |
| To select a source from the IRAM catalog of pointing sources, just type: | This command will produce a scan pattern as follows: |
| Line 139: | Line 172: |
| {{{ PAKO> source pointing_source /cat iram-J2000.sou }}} |
{{attachment:otf_example.png | OTF scan | width=500 }} |
| Line 143: | Line 174: |
=== Pointing === Choose a nearby quasar as pointing and focus source (using e.g. XEphem): {{{ PAKO> source 0133+476 /cat iram-J2000.sou }}} Launch the '''cont_pointing''' script: {{{ PAKO> @ cont_pointing }}} This script will launch a 1'x1' Lissajous map that takes 2 minutes. Once the pointing is finisihed, enter the pointings corrections: * For '''GISMO''', check in the PaKo display for the current pointing values (AZo and and ELo) and check in the [[ https://herapool.iram.es/GISMO/gismo.log.html | Nexus logsheet ]] for the corrections in azimuth and elevation (columns pnt.dAZ and pnt.dEL). To update the pointing constants type: {{{ PAKO> set pointing AZo+pnt.dAZ ELo+pnt.dEL }}} * For '''NIKA''' see the [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Continuum/NIKA/DataReduction | data reduction wiki ]] and ask the AoD. === Focus === The focus needs to be monitored and it needs to be corrected online! This should be done every three hours or so in the Z direction and every 12 hours in the X and Y directions. To check the quality of the focus, type: {{{ PAKO> @ cont_focusX Fx | PAKO> @ cont_focusY Fy | PAKO> @ cont_focusZ Fz }}} where Fx, Fy, and Fz are the current values of the focus in the X, Y, and Z direction, respectively. This script will send 5 1'x1' Lissajous maps performed with 5 different values of the focus. Each map will take 1 minute. Once the 5 scans are finished, follow these instructions to calculate the optimal value of the focus: * For '''GISMO''' open another terminal and use the corresponding python script: {{{ $ ssh -X mrt-lx3 $ cd Focus/ $ python FocusX.py s1 s2 s3 ... sn | $ python FocusY.py s1 s2 s3 ... sn | $ python FocusZ.py s1 s2 s3 ... sn }}} where s1 s2 s3 ... sn are the scans that the python script will use to estimate the new value of the focus. Check if the two estimates shown (see image below) in the plot are consistent. {{attachment:Focus.png|GISMO focus script|width=800}} * For '''NIKA''' see the [[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Continuum/NIKA/DataReduction | data reduction wiki ]] and ask the AoD. Finally, enter the new value: {{{ PAKO> set focus Fnew /dir X | PAKO> set focus Fnew /dir Y | PAKO> set focus Fnew /dir Z }}} Now the telescope is pointed and focussed, and ready to start to observe. === Science targets === Observations of science targets are performed via on-the-fly and/or Lissajous maps. For example, for a 16'x12' on-the-fly map, with a position angle of 25 degrees, a tilt angle of 0 degrees (both measured '''anticlockwise'''), in equatorial coordinates (radec), just type: {{{ PAKO> @ cont_onthefly 16 12 25 0 radec }}} For a 3'x3' Lissajous type: {{{ PAKO> @ cont_lissajous 3 }}} A sequence of several scans can be loaded using scripts. For example, the script [[attachment:observe_NGC4449.txt | observe_NGC4449.pako]] combines several 14'x14' on-the-fly maps at different angles in the horizontal coordinate system (azel). To launch this script just type: {{{ PAKO> @~/193-13/observe_NGC4449 }}} |
A sequence of several scans can be loaded using a script containing a sequence of '''nkotf''' maps. For example, the script [[attachment:observe2_NGC4449.txt | observe_NGC4449.pako]] combines several 10'x15' OTF maps at different PA and tilt angles in the horizontal coordinate system (azel). |
| Line 240: | Line 178: |
| == For technical staff == | Contact: Alessia Ritacco ([[http://www.iram.es/IRAMES/mainWiki/Continuum/NIKA2/Main|NIKA2]] Pool Manager of the 1st open pool) |
| Line 242: | Line 180: |
| email: ritaccoa@iram.es Created: 2013.OCT.25, by Isreal Hermelo |
|
| Line 243: | Line 184: |
| === Beam map === | Last update: 2017.FEB.05, by Pablo García |
| Line 245: | Line 186: |
| The beam map consists in a 5'x5' map with ~3" steps between rows and a duration ~18 min for GISMO, and 6.7'x3.7' map with 4" steps between rows and a duration ~12 min for NIKA. Beam maps are designed to ensure the source is moved over all the detectors of the array, in order to characterize and calibrate them (field of view geometry, flat field, stability...). The aim is to calculate the actual pixel offsets in the focal plane (see figure below). To obtain a beam map go to a primary calibrator and launch the '''cont_beammap.pako''' script: ## script for GISMO, and '''otfgeom.pako''' script for NIKA {{{ PAKO> @ cont_beammap }}} {{attachment:Beammap.png}} === Skydips === To run a skydip with the IRAM continuum cameras, launch the '''cont_skydip''' script: {{{ PAKO> @ cont_skydip }}} Please note that when using GISMO, before running a skydip, the observer has to de-activate the automatic relocking of the detectors: {{{ NEXUS -> Configuration -> Advanced -> De-activate automatic relock of detectors }}} And once the skydip is finished, the observer needs to switch-on by-hand the automatic relocking of the detectors: {{{ NEXUS -> Configuration -> Advanced -> Activate automatic relock of detectors }}} === Obsolete scripts === A set of fully tested scripts from previous runs are available within the '''~/PaKo/obs/''' folder. The following list shows how to launch some of the most ''popular'' obsolete scripts: {{{ GISMO PAKO> @ obs/gismo_pointing.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_2mx2m.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_3mx3m.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_4mx4m_2min.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_4mx4m.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_5mx5mfast.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_5mx5m.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_GDF.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_tiny1min.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_tiny2min.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_tiny4min.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_tiny5min.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_lissajous_tiny10min.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_otf_6mx6m.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_otf_8mx8m.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_otf_10mx10m.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_otf_30mx30m.pako PAKO> @ obs/gismo_otf_beammap.pako NIKA PAKO> @ obs/cross.pako PAKO> @ obs/diydown.pako PAKO> @ obs/diyup.pako PAKO> @ obs/faintliss1.pako PAKO> @ obs/faintliss1t.pako PAKO> @ obs/faintliss2.pako PAKO> @ obs/faintlissfast.pako PAKO> @ obs/faintliss.pako PAKO> @ obs/faintlisst.pako PAKO> @ obs/focusliss.pako PAKO> @ obs/focusp2.pako PAKO> @ obs/focusp.pako PAKO> @ obs/ngc891liss.pako PAKO> @ obs/otf10x10.pako PAKO> @ obs/otf10x2.pako PAKO> @ obs/otf15x10.pako PAKO> @ obs/otf3x3_el.pako PAKO> @ obs/otf3x3.pako PAKO> @ obs/otf4x2.pako PAKO> @ obs/otf4x4.pako PAKO> @ obs/otf5x5_half.pako PAKO> @ obs/otf5x5.pako PAKO> @ obs/otf5x5_pol.pako PAKO> @ obs/otf5x5slow.pako PAKO> @ obs/otfgeom.pako PAKO> @ obs/otfgeom_pol.pako PAKO> @ obs/otf.pako PAKO> @ obs/otfsz.pako PAKO> @ obs/pointliss.pako PAKO> @ obs/pointliss_pol.pako PAKO> @ obs/skydip.pako PAKO> @ obs/skydip_test.pako PAKO> @ obs/skydip_updown.pako PAKO> @ obs/skydip_up.pako }}} ----- Author: Israel Hermelo (IRAM 30m Continuum Pool Manager) email: hermelo@iram.es Created: 2013.Oct.25 Last update: 2014.Apr.22 |
Last update: 2017.SEP.28, by Alessia Ritacco |
Observing with NIKA2
Contents
Go to the NIKA2 main page.
Starting PaKo
To start the PaKo session for rgular obsevations, log into the pool account "nikas-17" (ask the AoD/operator for the login information), open a terminal and type:
$ ssh -X nikas-17-lx1 $ goNIKA $ PAKO> @ini $ PAKO> set project XXX $ PAKO> set doSubmit YES
Now you are ready to start observations.
Observations queue
To check what is currently in the observation's queue, open a terminal and type:
$ ssh -X mrt-lx1 $ observationQueue
This will open a file browser with a list of all the observation's files commanded, which are waiting to be executed by the telescope's system. To remove any observation's file from the queue, right-click on the corresponding xml file and select "delete". The display will be automatically refreshed.
Starting the NIKA2 pipeline
To have the IDL pipeline continuously processing observations as they are produced, open a terminal and type:
$ ssh -X observer@nika2-a (ask the AoD for the password) $ IDL IDL> nk_rta, scanID (e.g. '20151019s132')
where scanID is the corresponding identifier of the observation (as shown in the example) in the format YYYYMMDDsXXX, where YYYY is the year, MM the month, DD the day, and XXX the scan number.
Starting XEphem
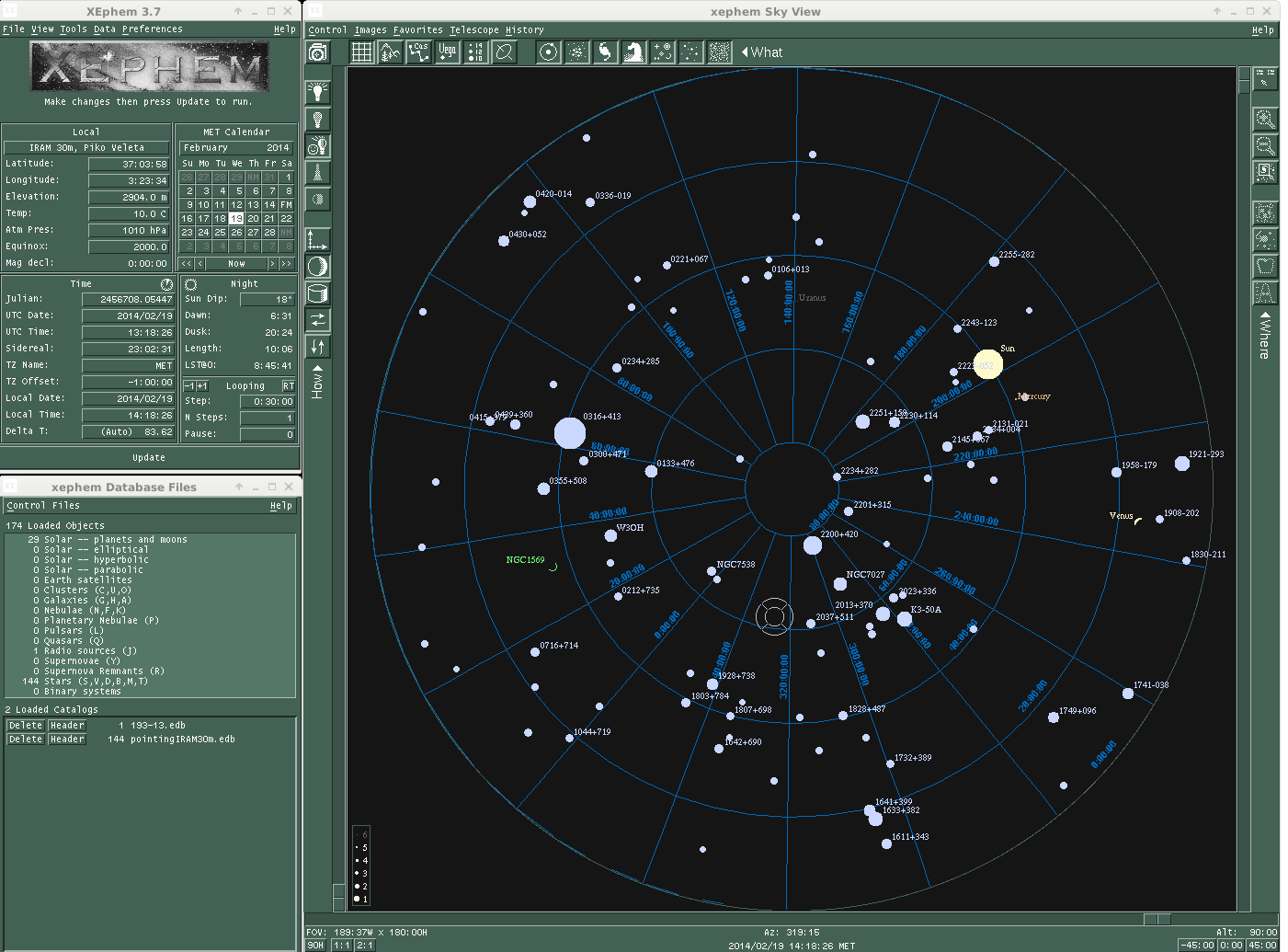
XEphem is the software currently used at the IRAM 30m telescope to keep track of the position of astronomical sources on the sky. To start XEphem, open a terminal and type:
$ ssh -X mrt-astro1 xephem or $ ssh -X mrt-lx3 $ xephem &
Then, click on the tab "View" and open the "Sky View". The "cross hair" shows the coordinates the telescope is pointing at. The filled blue circles are the pointing sources. The size of the circles is proportional to the flux of the target. To load the sources catalog of your project, click on the tab "Data" and go to "Files". In the new window go again to "Files" and select the catalog of the project that you are observing.
Pointing
In order to correct the pointing of the telescope in a given part of the sky choose a nearby pointing source (using e.g. XEphem) and type:
PAKO> source 0133+476 /cat * (or "iram-J2000.sou" for the given catalog)
Now launch the nkpoint script:
PAKO> @ nkpoint mode
where the keyword "mode" can adopt the values b for bright sources and f for faint sources (the l option for very faint sources that require the Lissajous pattern is no longer used). The pointing scans are currently reduced by the IDL pipeline. To obtain the pointing corrections, process the corresponding scan with the pipeline: "IDL> nk_rta, scanID". Once the pointing scan is processed, enter the new pointing corrections in azimuth (PnewX) and in elevation (PnewY) shown on the IDL prompt of the NIKA2 pipeline:
PAKO> set pointing PnewX PnewY
Focus
The focus needs to be monitored and it needs to be corrected online. This should be done every three hours or so in the Z direction. To check the quality of the focus run:
PAKO> @ focusOTF-Z fz
Currently, this script will carry out 5 foci measurements in Z direction within a 1.6 mm range, centered at the fz value. In order to obtain the focus corrections, the corresponding scan number have to be processed by the IDL pipeline:
IDL> nk_rta, scanID1 (for measurement 1) IDL> nk_rta, scanID2 (for measurement 2) IDL> nk_rta, scanID3 (for measurement 3) IDL> nk_rta, scanID4 (for measurement 4) IDL> nk_rta, scanID5 (for measurement 5)
Then, all measured foci need to be procesed together by the "nk_focus_otf" routine of the IDL pipeline to perform the best focus fit in terms of the mesured Flux, beam FWHM, and beam ellipticity of the KID's. This can be achieved by runnning the following instruction in the IDL prompt:
IDL> nk_focus_otf,'YYYYMMDDs'+strtrim(SCANNUMBER+indgen(5),2)
where the ScanID is in the format YYYYMMDDsSCANNUMBER (e.g. '20151019s132'). Once the "nk_focus_otf" routine has finished, check the focus correction values displayed in the IDL prompt under "Fluxes" for the three arrays (A1, A2, & A3) and calculate the average value that will be used to correct the focus. Enter the new focus value (Fnew) as follows:
PAKO> set focus Fnew
Beam map
Beam maps are designed to ensure the source is moved over all the detectors of the array, in order to characterize and calibrate them (field of view geometry, flat field, stability, etc). The aim is to calculate the actual pixel offsets in the focal plane (see figure below). To obtain a beam map go to a primary calibrator and launch the beammap1scan99sub.pako script in the normal PaKo session:
PAKO> @ beammap1scan99sub (to produce 99 sub-scans, standard PaKo version)
OPTION = a (ENTER OPTION: a = Az. scan, e = El. scan, l = lower than 60° in El., h = between 60° and 70° in El.)
W-OTFMAP /TOTF, value 12.0 implies /speed 65.0 outside standard range 0.0 to 60.0
W-OTFMAP, WARNING--CONDITION: Elevation must be less than 69.03 [deg]
OTFMAP 780''x 470.4'' (step 4.8)
> Number of subscans: 99
> Scanning speed: 65 arcsec/sec
> Time per subscan: 12 sec
> Execution time: 23.1 min 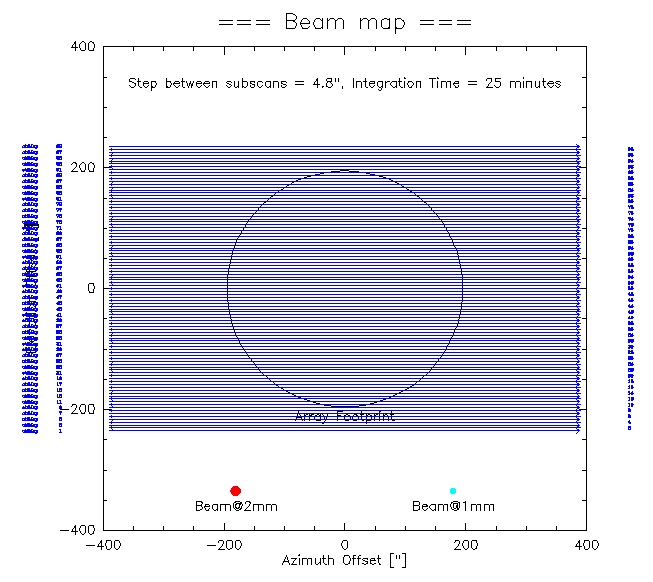
Skydips
To run a skydip with NIKA2 type in PaKo:
PAKO> @ skydip
The script will perform 11 measurements (30 [s] tracks) at different airmasses wrt. the position Az = 180°, El = 55° in the HORIZON coordinate system. The skydip takes ~6.4 minutes to be finished.
Science targets
Observations of science targets are performed via on-the-fly (OTF). For example, for a 10'x15' OTF map, with a position angle of 25 degrees, a tilt angle of 0 degrees (both measured anticlockwise), in equatorial coordinates (radec, for the HORIZON coordinate system set azel), just type:
PAKO> @nkotf 10 15 25 0 20 40 radec
This command will produce a scan pattern as follows:
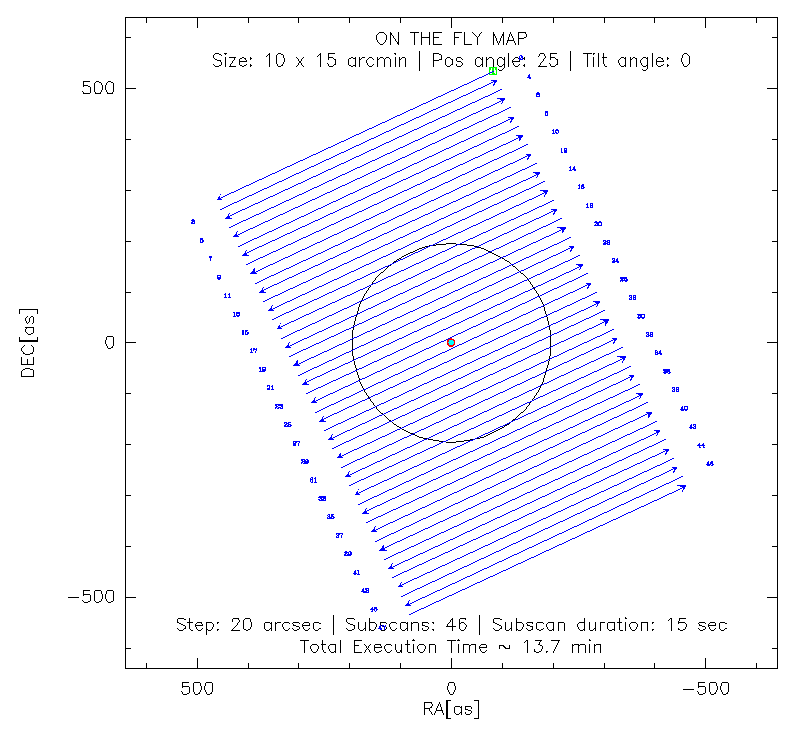
A sequence of several scans can be loaded using a script containing a sequence of nkotf maps. For example, the script observe_NGC4449.pako combines several 10'x15' OTF maps at different PA and tilt angles in the horizontal coordinate system (azel).
Contact: Alessia Ritacco (NIKA2 Pool Manager of the 1st open pool)
email: ritaccoa@iram.es
Created: 2013.OCT.25, by Isreal Hermelo
Last update: 2017.FEB.05, by Pablo García
Last update: 2017.SEP.28, by Alessia Ritacco
