|
Size: 3390
Comment:
|
Size: 4415
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| ##acl NicolasBillot,hermelo,CarstenKramer,SamuelLeclerc:read,write,delete,revert,admin Default | ##acl hermelo,CarstenKramer,NicolasBillot,SamuelLeclerc:read,write,delete,revert,admin Default |
| Line 10: | Line 10: |
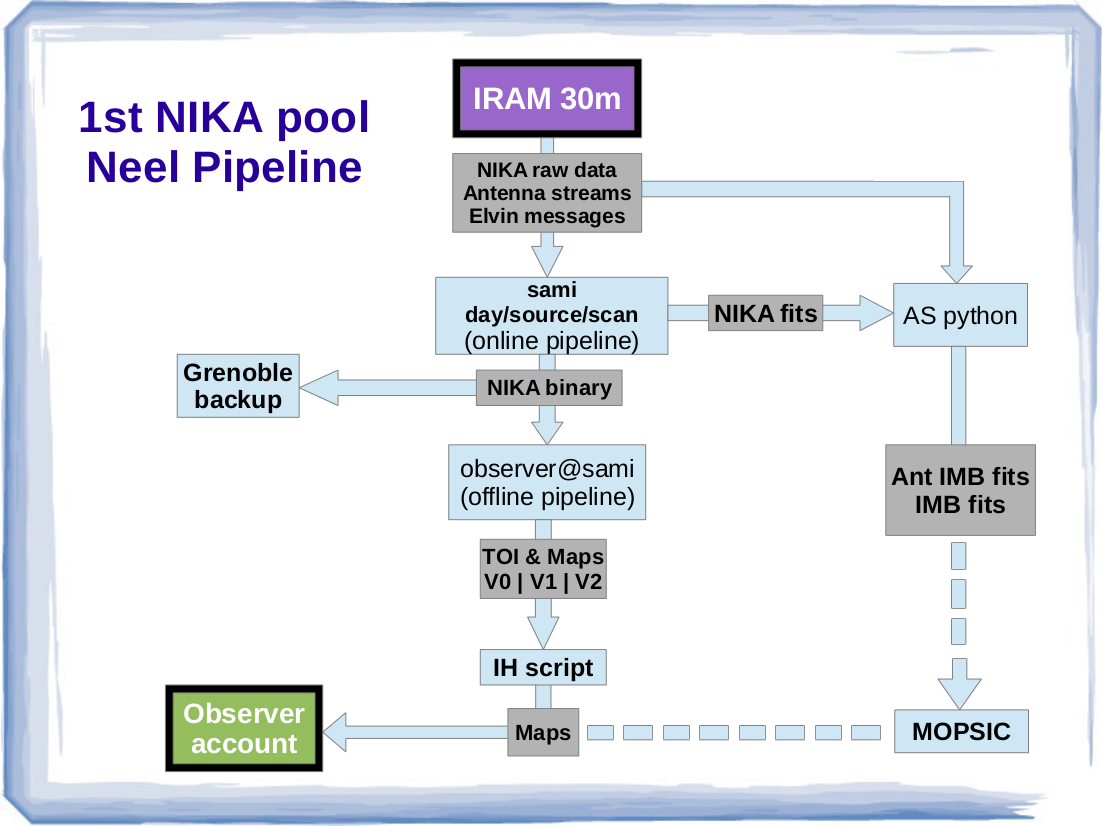
== Neel pipeline == The following diagram shows the NIKA data flow from the IRAM 30m telescope to the observers' accounts. {{attachment:NIKApipeline.png|alt text|height=600}} |
|
| Line 36: | Line 43: |
| * In the emacs window, edit run pointing.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. | * In the emacs window, edit run_pointing.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. |
| Line 39: | Line 46: |
| * In the idl session in T2, type .r run pointing * Several plot windows might be on top of eachother * Follow instructions returned by the code in T2. By default, follow instructions “B (2mm) : (MAP) (for PAKO and pointing model)”. |
* In the idl session, type .r run_pointing * Several plot windows might be on top of each other * Follow instructions returned by the code in the terminal. By default, follow instructions “B (2mm) : (MAP) (for PAKO and pointing model)”. |
| Line 45: | Line 52: |
| * In the emacs window, edit run pointing liss.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. | * In the emacs window, edit run_pointing_liss.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. |
| Line 47: | Line 54: |
| * In the idl session in T2, type .r run pointing liss * Several plot windows might be on top of eachother * Follow instructions returned by the code in T2 |
* In the idl session, type .r run_pointing_liss * Several plot windows might be on top of each other * Follow instructions returned by the code in the terminal |
| Line 53: | Line 60: |
| * In the emacs window, edit run focus.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. | * In the emacs window, edit run_focus.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. |
| Line 57: | Line 64: |
| * In the idl session in T2, type .r run focus * Several plot windows might be on top of eachother * Follow instructions returned by the code in T2 |
* In the idl session, type .r run_focus * Several plot windows might be on top of each other * Follow instructions returned by the code in the terminal |
| Line 63: | Line 70: |
| * In the emacs window, edit run focus liss.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. Scan num should be the first of the five scans involved in this analysis. | * In the emacs window, edit run focus_liss.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. Scan num should be the first of the five scans involved in this analysis. |
| Line 65: | Line 72: |
| * In the idl session in T2, type .r run focus liss * Several plot windows might be on top of eachother * Follow instructions returned by the code in T2 |
* In the idl session in T2, type .r run_focus_liss * Several plot windows might be on top of each other * Follow instructions returned by the code in the terminal |
| Line 71: | Line 78: |
| * In the emacs window, edit run skydip.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. | * In the emacs window, edit run_skydip.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. |
| Line 73: | Line 80: |
| * In the idl session in T2, type .r run skydip * Several plot windows might be on top of eachother * Follow instructions returned by the code in T2 |
* In the idl session, type .r run_skydip * Several plot windows might be on top of each other * Follow instructions returned by the code in the terminal |
| Line 79: | Line 86: |
| * In the emacs window, edit run otf geometry.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. | * In the emacs window, edit run_otf_geometry.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. |
| Line 81: | Line 88: |
| * In the idl session in T2, type .r run otg geometry * Several plot windows might be on top of eachother * Follow instructions returned by the code in T2 |
* In the idl session in T2, type .r run_otf_geometry * Several plot windows might be on top of each other * Follow instructions returned by the code in the terminal |
| Line 88: | Line 95: |
| The science scans are meant to be optimally processed offline with tailored procedures. The real time software mentioned in this note only aims at giving a quick feedback | The science scans are meant to be optimally processed offline with tailored procedures. The real time software mentioned in this note only aims at giving a quick feedback. === Total power maps === All maps (On-the-Fly and Lissajous) in '''Total Power Mode''' can be reduced by the same script: * In the emacs window, edit run_otf_map.pro and update the scan num and day parameters. * If you’re observing a point source, set diffuse = 0. If you’re observing diffuse emission set diffuse = 1. * Save the file * In the idl session, type .r run_otf_map * Several plot windows might be on top of each other === Polarization maps === All maps (On-the-Fly and Lissajous) in '''Polarization Mode''' can be reduced by the same script: * In the emacs window, edit run_otf_polar_maps.pro and update the scan num and day parameters. * Save the file * In the idl session, type .r run_otf_polar_maps * Several plot windows might be on top of each other == Data products == [[ http://www.iram.fr/wiki/nika2/index.php/NIKARun8productv2 | Data products for the 1st NIKA pool ]] |
| Line 91: | Line 121: |
Author: Israel Hermelo (IRAM 30m continuum pool manager) email: hermelo@iram.es Created: 2014.02.06 Last update: 2014.02.06 |
NIKA Data Reduction
Contents
Neel pipeline
The following diagram shows the NIKA data flow from the IRAM 30m telescope to the observers' accounts.
Getting ready
To start the IDL session for the real time analysis, open a terminal and type: analaysis.
$ ssh -X nikaw-13@mrt-lx1 $ ssh_sami > rt > emacs & > idl
Shortly after a scan is done, the NIKA scientific data and the AntennaIMBfits are written on SAMI and can be processed. There are two types of observation: the “science” scans and the “calibration” scans. There is a specific routine to analyze each type of scan.
Calibration scans
The calibration scans expect actions from the observer and interaction with PaKo.
cont_pointing_cross
- In the emacs window, edit run_pointing.pro and update the day and scan num parameters.
- update the p2cor and p7cor parameters with the “SET POINTING” values displayed in the PAKO window.
- Save the file
- In the idl session, type .r run_pointing
- Several plot windows might be on top of each other
- Follow instructions returned by the code in the terminal. By default, follow instructions “B (2mm) : (MAP) (for PAKO and pointing model)”.
cont_pointing_liss
- In the emacs window, edit run_pointing_liss.pro and update the day and scan num parameters.
- Save the file
- In the idl session, type .r run_pointing_liss
- Several plot windows might be on top of each other
- Follow instructions returned by the code in the terminal
cont_focus_track
- In the emacs window, edit run_focus.pro and update the day and scan num parameters.
- Check the value of focusz in the PAKO display window.
- Do not change the fooffset values unless you have modified the pako script focusp.pako.
- Save the file
- In the idl session, type .r run_focus
- Several plot windows might be on top of each other
- Follow instructions returned by the code in the terminal
cont_focus_liss
- In the emacs window, edit run focus_liss.pro and update the day and scan num parameters. Scan num should be the first of the five scans involved in this analysis.
- Save the file
- In the idl session in T2, type .r run_focus_liss
- Several plot windows might be on top of each other
- Follow instructions returned by the code in the terminal
cont_skydip
- In the emacs window, edit run_skydip.pro and update the day and scan num parameters.
- Save the file
- In the idl session, type .r run_skydip
- Several plot windows might be on top of each other
- Follow instructions returned by the code in the terminal
cont_beammap
- In the emacs window, edit run_otf_geometry.pro and update the day and scan num parameters.
- Save the file
- In the idl session in T2, type .r run_otf_geometry
- Several plot windows might be on top of each other
- Follow instructions returned by the code in the terminal
Science scans
The science scans are meant to be optimally processed offline with tailored procedures. The real time software mentioned in this note only aims at giving a quick feedback.
Total power maps
All maps (On-the-Fly and Lissajous) in Total Power Mode can be reduced by the same script:
- In the emacs window, edit run_otf_map.pro and update the scan num and day parameters.
- If you’re observing a point source, set diffuse = 0. If you’re observing diffuse emission set diffuse = 1.
- Save the file
- In the idl session, type .r run_otf_map
- Several plot windows might be on top of each other
Polarization maps
All maps (On-the-Fly and Lissajous) in Polarization Mode can be reduced by the same script:
- In the emacs window, edit run_otf_polar_maps.pro and update the scan num and day parameters.
- Save the file
- In the idl session, type .r run_otf_polar_maps
- Several plot windows might be on top of each other
Data products
Data products for the 1st NIKA pool
